 Home
Home
 Back
Back
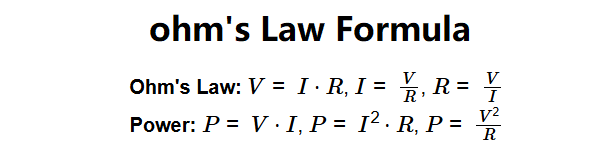
Definition: This calculator uses Ohm's Law and power equations to compute power (P), current (I), voltage (V), and resistance (R) in a DC or single-phase AC circuit, given any two known values.
Purpose: It is used in electrical engineering and electronics to design circuits, select components, and analyze circuit behavior.
The calculator applies Ohm's Law and power formulas:
Where:
Steps:
Details: These calculations are fundamental for designing safe and efficient electrical circuits, ensuring proper component ratings, and preventing overloads or failures in electronics and power systems.
Tips: Enter exactly two positive values. Select appropriate units (e.g., mA for small currents, kV for high voltages). The calculator handles unit conversions automatically. For AC circuits, use RMS values for voltage and current.
Examples:
The following table provides quick reference calculations for common voltage and current values:
| Voltage (V) | Current (A) | Power (W) | Resistance (Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 10 |
| 12 | 2 | 24 | 6 |
| 230 | 0.23 | 52.9 | 1000 |
| 110 | 5 | 550 | 22 |
Use this table for quick lookups or to verify calculator results.
Q: What is Ohm's Law?
A: Ohm's Law states that the current through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across it, with resistance as the constant of proportionality (\( V = I \cdot R \)).
Q: Can this calculator be used for AC circuits?
A: Yes, for single-phase AC circuits, use RMS values for voltage and current. It does not account for power factor or three-phase systems.
Q: Why do I need to enter exactly two values?
A: The equations require two known variables to solve for the other two uniquely. Entering more or fewer values leads to ambiguous or impossible solutions.
Q: What happens if I enter negative values?
A: Negative values are invalid for these calculations, as power, current, voltage, and resistance are positive quantities in this context.
Q: How are units handled?
A: The calculator converts inputs to base units (W, A, V, Ω) for calculations and converts results back to the selected units, ensuring flexibility for various scales (e.g., mA for small currents, kV for high voltages).