1. What is the Absolute Humidity to Relative Humidity Calculator?
Definition: This calculator determines the relative humidity (\( RH \)) and actual vapor pressure (\( P_a \)) of air based on the absolute humidity (\( AH \)) and air temperature (\( T \)). Relative humidity is the percentage of water vapor in the air compared to the maximum amount the air can hold at a given temperature.
Purpose: It is used in meteorology, HVAC engineering, and environmental science to assess moisture levels for weather forecasting, indoor climate control, and industrial processes.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas
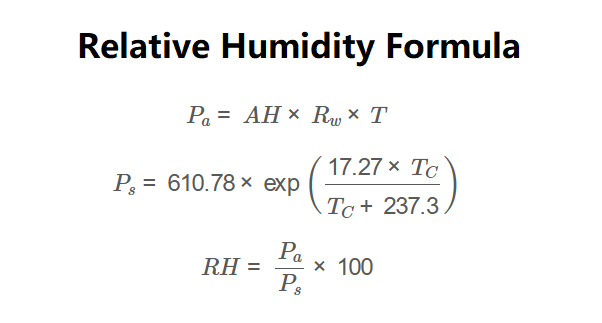
Formulas:
\[
P_a = AH \times R_w \times T
\]
\[
P_s = 610.78 \times \exp\left(\frac{17.27 \times T_C}{T_C + 237.3}\right)
\]
\[
RH = \frac{P_a}{P_s} \times 100
\]
where:
- \( RH \): Relative humidity (%)
- \( P_a \): Actual vapor pressure (Pa, bar, psi, at, atm, Torr, hPa, kPa, lb/ft²)
- \( AH \): Absolute humidity (kg/m³, g/m³, lb/ft³)
- \( P_s \): Saturation vapor pressure (Pa)
- \( R_w \): Specific gas constant for water vapor, 461.5 J/(kg·K)
- \( T \): Temperature in Kelvin (K)
- \( T_C \): Temperature in °C
Unit Conversions:
- Temperature (\( T \)):
- 1 °C = 273.15 K
- 1 °F = (T - 32) × 5/9 + 273.15 K
- 1 K = 1 K
- Absolute Humidity (\( AH \)):
- 1 kg/m³ = 1 kg/m³
- 1 g/m³ = 0.001 kg/m³
- 1 lb/ft³ = 16.0185 kg/m³
- Actual Vapor Pressure (\( P_a \)):
- 1 Pa = 1 Pa
- 1 bar = 100000 Pa
- 1 psi = 6894.76 Pa
- 1 at = 98066.5 Pa
- 1 atm = 101325 Pa
- 1 Torr = 133.322 Pa
- 1 hPa = 100 Pa
- 1 kPa = 1000 Pa
- 1 lb/ft² = 47.8803 Pa
Steps:
- Enter the absolute humidity (\( AH \)) in g/m³, kg/m³, or lb/ft³ (default is 20.278 g/m³, step size 0.00001).
- Enter the air temperature (\( T \)) in °C, °F, or K (default is 32°C, step size 0.00001).
- Convert \( AH \) to kg/m³ and \( T \) to Kelvin and °C.
- Calculate the actual vapor pressure (\( P_a \)) using \( P_a = AH \times R_w \times T \).
- Calculate the saturation vapor pressure (\( P_s \)) using the Magnus-Tetens approximation.
- Calculate the relative humidity (\( RH \)) using \( RH = \frac{P_a}{P_s} \times 100 \).
- Convert \( P_a \) to the selected unit and display results, using scientific notation if the absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise rounded to 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Relative Humidity Calculation
- Comfort: High relative humidity makes air feel muggy, reducing sweat evaporation and increasing perceived temperature.
- Meteorology: Predicting precipitation, fog, or dew formation.
- Industry: Controlling moisture in manufacturing, storage, and HVAC systems for quality and efficiency.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: Calculate the relative humidity and actual vapor pressure for air with an absolute humidity of 20.278 g/m³ and temperature of 32°C, with actual vapor pressure in Pa
- Enter \( AH = 20.278 \) g/m³, convert to kg/m³: \( 20.278 \times 0.001 = 0.020278 \, \text{kg/m}^3 \).
- Enter \( T = 32 \) °C, convert to K: \( 32 + 273.15 = 305.15 \, \text{K} \).
- Actual vapor pressure: \( P_a = 0.020278 \times 461.5 \times 305.15 \approx 2856.03 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Saturation vapor pressure: \( P_s = 610.78 \times \exp\left(\frac{17.27 \times 32}{32 + 237.3}\right) \approx 4759.76 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Relative humidity: \( RH = \frac{2856.03}{4759.76} \times 100 \approx 60.0000 \, \% \).
- Result: \( RH = 60.0000 \, \% \), \( P_a = 2856.0300 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Example 2: Calculate the relative humidity and actual vapor pressure for air with an absolute humidity of 0.002134 g/m³ and temperature of -10°C, with actual vapor pressure in psi:
- Enter \( AH = 0.002134 \) g/m³, convert to kg/m³: \( 0.002134 \times 0.001 = 0.000002134 \, \text{kg/m}^3 \).
- Enter \( T = -10 \) °C, convert to K: \( -10 + 273.15 = 263.15 \, \text{K} \).
- Actual vapor pressure: \( P_a = 0.000002134 \times 461.5 \times 263.15 \approx 259.05 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Saturation vapor pressure: \( P_s = 610.78 \times \exp\left(\frac{17.27 \times (-10)}{-10 + 237.3}\right) \approx 259.05 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Relative humidity: \( RH = \frac{259.05}{259.05} \times 100 \approx 100.0000 \, \% \).
- Convert \( P_a \) to psi: \( 259.05 \times 0.000145038 \approx 0.0376 \), use scientific notation: \( 3.7563 \times 10^{-5} \).
- Result: \( RH = 100.0000 \, \% \), \( P_a = 3.7563 \times 10^{-5} \, \text{psi} \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is relative humidity?
A: Relative humidity is the percentage of water vapor in the air compared to the maximum amount the air can hold at a given temperature. It affects comfort and weather conditions.
Q: How does absolute humidity relate to relative humidity?
A: Absolute humidity measures the mass of water vapor per unit volume of air, while relative humidity expresses this as a percentage of the maximum possible at a given temperature.
Q: Why use the Magnus-Tetens approximation?
A: The Magnus-Tetens formula provides a simple and accurate way to estimate saturation vapor pressure for typical atmospheric conditions, making it suitable for humidity calculations.
Absolute Humidity to Relative Humidity Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back