 Home
Home
 Back
Back
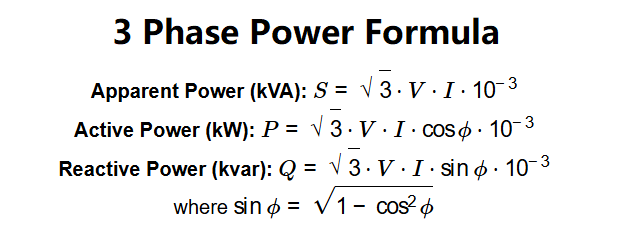
Definition: This calculator computes the apparent power (kVA), active power (kW), and reactive power (kvar) for a balanced three-phase AC system based on line-to-line voltage, current, and power factor.
Purpose: It is used in electrical engineering to analyze power consumption, size equipment, and optimize energy efficiency in industrial and commercial applications.
The calculator uses the following formulas for a balanced three-phase system:
Where:
Steps:
Details: Accurate power calculations ensure proper sizing of transformers, generators, and cables, prevent overloads, and optimize energy efficiency in three-phase systems, which are common in industrial and commercial settings.
Tips: Input positive values for voltage and current. Use realistic power factor values (e.g., 0.8–0.95 for motors, 1 for resistive loads). Select appropriate units for voltage and current based on your system (e.g., kV for high-voltage systems, mA for small currents).
Example: Calculate power for \( V = 400 \, \text{V} \), \( I = 20 \, \text{A} \), \( \cos \phi = 0.85 \).
The following table provides quick reference power calculations for common voltage and current values (\( \cos \phi = 0.85 \)):
| Voltage (V) | Current (A) | Apparent Power (kVA) | Active Power (kW) | Reactive Power (kvar) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | 10 | 6.92820 | 5.88897 | 3.65052 |
| 400 | 20 | 13.85641 | 11.77875 | 7.30104 |
| 480 | 15 | 12.47044 | 10.59988 | 6.57194 |
| 11,000 | 50 | 952.62794 | 809.73375 | 502.07476 |
Use this table for quick lookups or to verify calculator results.
Q: What is the difference between apparent, active, and reactive power?
A: Apparent power (kVA) is the total power in the circuit, active power (kW) is the power consumed by the load, and reactive power (kvar) is the power stored and returned due to inductive or capacitive elements.
Q: Why is the power factor important?
A: The power factor indicates the efficiency of power usage. A lower power factor means more reactive power, increasing losses and requiring larger equipment.
Q: What voltage and current units should I use?
A: Use units appropriate for your system (e.g., kV for high-voltage grids, mA for small currents). The calculator converts them automatically to volts and amps.
Q: Does this calculator work for unbalanced systems?
A: No, this calculator assumes a balanced three-phase system where all phases have equal voltage, current, and power factor.