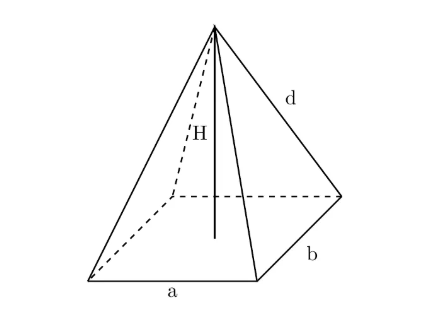
1. What is a Right Rectangular Pyramid Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the geometric properties of a right rectangular pyramid, including base surface area (\( A_b \)), lateral surface area (\( A_l \)), pyramid height (\( H \)), total surface area (\( A \)), volume (\( V \)), base diagonal, first and second slant heights, and areas of the lateral faces, given the base length (\( a \)), base width (\( b \)), and lateral edge (\( d \)). A right rectangular pyramid has a rectangular base and an apex directly above the base’s center, with four triangular lateral faces.
Purpose: It aids in calculations for geometry education, architecture, and engineering, such as determining material needs for pyramid-shaped structures or analyzing their volumes.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
- Pyramid height \( H \): \( H = \sqrt{d^2 - \frac{a^2 + b^2}{4}} \).
- Base diagonal: \( \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \).
- First slant height: \( s_1 = \sqrt{\left(\frac{a}{2}\right)^2 + H^2} \).
- Second slant height: \( s_2 = \sqrt{\left(\frac{b}{2}\right)^2 + H^2} \).
- Base surface area \( A_b \): \( A_b = a \times b \).
- First lateral face area: \( \text{Area}_1 = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times s_1 \).
- Second lateral face area: \( \text{Area}_2 = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times s_2 \).
- Lateral surface area \( A_l \): \( A_l = 2 \times (\text{Area}_1 + \text{Area}_2) \).
- Total surface area \( A \): \( A = A_b + A_l \).
- Volume \( V \): \( V = \frac{1}{3} \times a \times b \times H \).
Unit Conversions:
- Length Units: m, cm (1 m = 100 cm), mm (1 m = 1000 mm), in (1 m = 39.3701 in), ft (1 m = 3.28084 ft), yd (1 m = 1.09361 yd).
- Area Units: m², cm² (1 m² = 10000 cm²), mm² (1 m² = 1000000 mm²), in² (1 m² = 1550.0031 in²), ft² (1 m² = 10.7639 ft²), yd² (1 m² = 1.19599 yd²).
- Volume Units: m³, cm³ (1 m³ = 1000000 cm³), mm³ (1 m³ = 1000000000 mm³), in³ (1 m³ = 61023.7441 in³), ft³ (1 m³ = 35.3147 ft³), yd³ (1 m³ = 1.30795 yd³).
Steps:
- Input the base length \( a \), base width \( b \), and lateral edge \( d \), and select their units.
- Validate inputs (must be positive, and \( d^2 > \frac{a^2 + b^2}{4} \)).
- Convert inputs to meters for calculations.
- Compute the height, diagonal, slant heights, areas, and volume using the formulas above.
- Convert outputs to the selected units.
- Format outputs to 4 decimal places or scientific notation for small values.
3. Importance of Rectangular Pyramid Calculations
Calculating pyramid properties is essential for:
- Geometry Education: Understanding three-dimensional shapes and their properties.
- Architecture and Design: Designing pyramid-shaped structures, such as roofs or monuments.
- Engineering: Analyzing material requirements and structural properties for pyramid-based designs.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: Base length \( a = 6 \, \text{cm} \), Base width \( b = 8 \, \text{cm} \), Lateral edge \( d = 10 \, \text{cm} \)
- Convert: \( a = 0.06 \, \text{m} \), \( b = 0.08 \, \text{m} \), \( d = 0.1 \, \text{m} \).
- Base diagonal: \( \sqrt{0.06^2 + 0.08^2} \approx 0.1 \, \text{m} = 10.0000 \, \text{cm} \).
- Pyramid height: \( H = \sqrt{0.1^2 - \frac{0.06^2 + 0.08^2}{4}} \approx 0.08 \, \text{m} = 8.0000 \, \text{cm} \).
- First slant height: \( s_1 = \sqrt{\left(\frac{0.06}{2}\right)^2 + 0.08^2} \approx 0.0854 \, \text{m} = 8.5440 \, \text{cm} \).
- Second slant height: \( s_2 = \sqrt{\left(\frac{0.08}{2}\right)^2 + 0.08^2} \approx 0.0894 \, \text{m} = 8.9443 \, \text{cm} \).
- Base surface area: \( A_b = 0.06 \times 0.08 \approx 0.0048 \, \text{m}^2 = 48.0000 \, \text{cm}^2 \).
- First lateral face area: \( \text{Area}_1 = \frac{1}{2} \times 0.08 \times 0-0.0854 \approx 0.0034 \, \text{m}^2 = 34.1761 \, \text{cm}^2 \).
- Second lateral face area: \( \text{Area}_2 = \frac{1}{2} \times 0.06 \times 0.0894 \approx 0.0027 \, \text{m}^2 = 26.8328 \, \text{cm}^2 \).
- Lateral surface area: \( A_l = 2 \times (0.0034 + 0.0027) \approx 0.0122 \, \text{m}^2 = 122.0178 \, \text{cm}^2 \).
- Total surface area: \( A = 0.0048 + 0.0122 \approx 0.0170 \, \text{m}^2 = 170.0178 \, \text{cm}^2 \).
- Volume: \( V = \frac{1}{3} \times 0.0048 \times 0.08 \approx 0.000128 \, \text{m}^3 = 128.0000 \, \text{cm}^3 \).
- Example 2: Base length \( a = 3 \, \text{m} \), Base width \( b = 4 \, \text{m} \), Lateral edge \( d = 5 \, \text{m} \)
- Base diagonal: \( \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} \approx 5 \, \text{m} \).
- Pyramid height: \( H = \sqrt{5^2 - \frac{3^2 + 4^2}{4}} \approx 4 \, \text{m} \).
- First slant height: \( s_1 = \sqrt{\left(\frac{3}{2}\right)^2 + 4^2} \approx 4.2720 \, \text{m} \).
- Second slant height: \( s_2 = \sqrt{\left(\frac{4}{2}\right)^2 + 4^2} \approx 4.4721 \, \text{m} \).
- Base surface area: \( A_b = 3 \times 4 = 12 \, \text{m}^2 \).
- First lateral face area: \( \text{Area}_1 = \frac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 4.2720 \approx 8.5440 \, \text{m}^2 \).
- Second lateral face area: \( \text{Area}_2 = \frac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 4.4721 \approx 6.7082 \, \text{m}^2 \).
- Lateral surface area: \( A_l = 2 \times (8.5440 + 6.7082) \approx 30.5044 \, \text{m}^2 \).
- Total surface area: \( A = 12 + 30.5044 \approx 42.5044 \, \text{m}^2 \).
- Volume: \( V = \frac{1}{3} \times 12 \times 4 \approx 16 \, \text{m}^3 \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a right rectangular pyramid?
A: A right rectangular pyramid is a three-dimensional shape with a rectangular base and an apex directly above the base’s center, connected by four triangular lateral faces.
Q: What are the first and second slant heights?
A: The first slant height is the height of the triangular faces perpendicular to the base length (\( a \)), and the second is for the faces perpendicular to the base width (\( b \)).
Q: Why must the lateral edge be sufficiently long?
A: The lateral edge (\( d \)) must satisfy \( d^2 > \frac{a^2 + b^2}{4} \) to ensure a positive pyramid height, as it forms the hypotenuse of a right triangle with the height and half the base diagonal.
Right Rectangular Pyramid Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back