1. What is the Warsaw Method Calculator?
Definition: This calculator uses the Warsaw Method to estimate the insulin dose required for meals high in fat and protein by converting their caloric content into a carbohydrate equivalent and calculating Fat-Protein Units (FPU).
Purpose: It helps individuals with diabetes, particularly those on insulin therapy, calculate the appropriate insulin dose for meals that contain significant amounts of fat and protein, which can delay glucose absorption and require an extended bolus.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator follows these steps to compute the insulin dose:
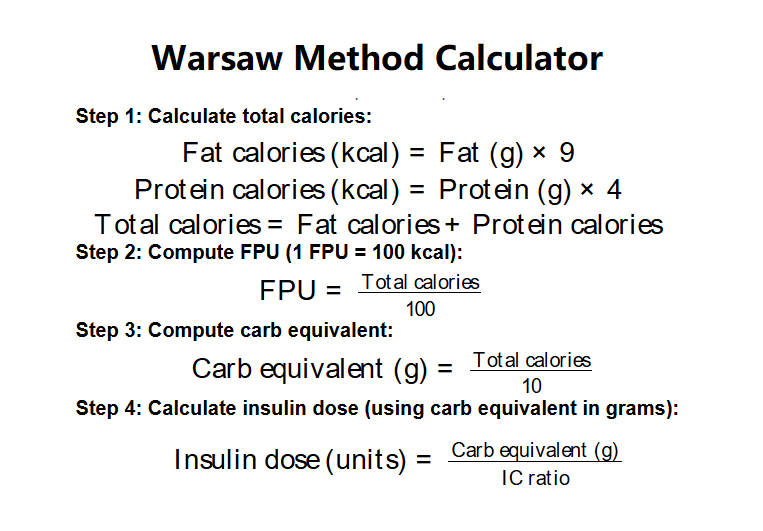
- Step 1: Calculate total calories:
\( \text{Fat calories (kcal)} = \text{Fat (g)} \times 9 \)
\( \text{Protein calories (kcal)} = \text{Protein (g)} \times 4 \)
\( \text{Total calories} = \text{Fat calories} + \text{Protein calories} \)
- Step 2: Compute FPU (1 FPU = 100 kcal):
\( \text{FPU} = \frac{\text{Total calories}}{100} \)
- Step 3: Compute carb equivalent:
\( \text{Carb equivalent (g)} = \frac{\text{Total calories}}{10} \)
- Step 4: Calculate insulin dose (using carb equivalent in grams):
\( \text{Insulin dose (units)} = \frac{\text{Carb equivalent (g)}}{\text{IC ratio}} \)
- Step 5: Extended bolus:
- In this context, the extended bolus is the same as the insulin dose, typically administered over an extended period for meals high in fat and protein.
Inputs:
- Fat (mg, g, kg, lb, oz)
- Protein (mg, g, kg, lb, oz)
- Insulin-to-Carb Ratio (IC ratio)
Unit Conversions:
- Fat and Protein: mg, g, kg, lb, oz (1 g = 1000 mg, 1 kg = 1000 g, 1 lb = 453.592 g, 1 oz = 28.3495 g)
- Carb Equivalent: mg, g, kg, lb, oz (1 g = 1000 mg, 1 kg = 1000 g, 1 lb = 453.592 g, 1 oz = 28.3495 g)
Steps:
- Input the amount of fat and select its unit.
- Input the amount of protein and select its unit.
- Input your insulin-to-carb ratio (IC ratio).
- Compute the total calories, FPU, carb equivalent, insulin dose, and extended bolus.
- Adjust the carb equivalent unit as needed using the dropdown.
3. Importance of Warsaw Method Calculations
The Warsaw Method calculation is useful for:
- Diabetes Management: Helps individuals with diabetes calculate insulin doses for meals high in fat and protein, which can cause delayed glucose spikes.
- Extended Bolus Planning: Provides a method to determine the insulin dose that can be administered as an extended bolus, improving blood sugar control for mixed meals.
- Personalized Dosing: Accounts for individual insulin sensitivity through the IC ratio, ensuring more accurate insulin dosing.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Fat 20 g, Protein 30 g, IC Ratio 5:
Fat calories: \( 20 \times 9 = 180 \, \text{kcal} \).
Protein calories: \( 30 \times 4 = 120 \, \text{kcal} \).
Total calories: \( 180 + 120 = 300 \, \text{kcal} \).
FPU: \( \frac{300}{100} = 3.00 \, \text{FPU} \).
Carb equivalent: \( \frac{300}{10} = 30.00 \, \text{g} \).
Carb equivalent in mg: \( 30.00 \times 1000 = 30000.00 \, \text{mg} \).
Insulin dose: \( \frac{30}{5} = 6.00 \, \text{units} \).
Extended bolus: \( 6.00 \, \text{units} \).
- Fat 0.01 kg, Protein 500 mg, IC Ratio 8:
Fat in g: \( 0.01 \times 1000 = 10 \, \text{g} \).
Protein in g: \( 500 \div 1000 = 0.5 \, \text{g} \).
Fat calories: \( 10 \times 9 = 90 \, \text{kcal} \).
Protein calories: \( 0.5 \times 4 = 2 \, \text{kcal} \).
Total calories: \( 90 + 2 = 92 \, \text{kcal} \).
FPU: \( \frac{92}{100} = 0.92 \, \text{FPU} \).
Carb equivalent: \( \frac{92}{10} = 9.20 \, \text{g} \).
Carb equivalent in oz: \( 9.20 \div 28.3495 \approx 0.32 \, \text{oz} \).
Insulin dose: \( \frac{9.20}{8} = 1.15 \, \text{units} \).
Extended bolus: \( 1.15 \, \text{units} \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the Warsaw Method?
A: The Warsaw Method is a technique used in diabetes management to calculate insulin doses for meals high in fat and protein by converting their caloric content into a carbohydrate equivalent, which is then used to determine the insulin dose.
Q: What is an FPU?
A: FPU (Fat-Protein Unit) represents the energy content of fat and protein in a meal, where 1 FPU equals 100 kcal. It is used to estimate the insulin requirements for mixed meals.
Q: What is an extended bolus?
A: An extended bolus is an insulin delivery method where the insulin dose is administered over an extended period (e.g., several hours) rather than all at once, often used for meals high in fat and protein that cause delayed glucose absorption.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back