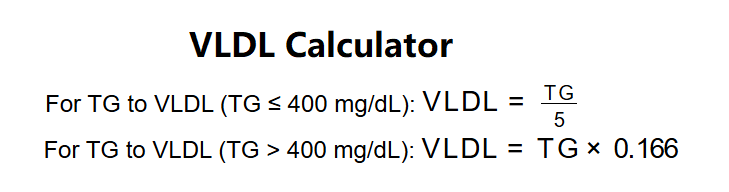1. What is a VLDL Calculator?
Definition: This calculator converts between Triglycerides (TG) and Very Low-Density Lipoprotein (VLDL) levels using equations developed by Friedewald and collaborators, and Wilson et al. for high TG levels.
Purpose: It helps users estimate VLDL from TG or vice versa, providing insights into lipid levels that are associated with cardiovascular risk.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
For TG to VLDL (TG ≤ 400 mg/dL): \( \text{VLDL} = \frac{\text{TG}}{5} \)
For TG to VLDL (TG > 400 mg/dL): \( \text{VLDL} = \text{TG} \times 0.166 \)
For VLDL to TG (mg/dL): \( \text{TG} = \text{VLDL} \times 5 \)
For VLDL to TG (mmol/L): \( \text{TG} = \frac{\text{VLDL}}{0.166} \)
Unit Conversions:
- Triglycerides and VLDL: \( \text{mmol/L} = \frac{\text{mg/dL}}{88.57} \), \( \text{mg/dL} = \text{mmol/L} \times 88.57 \)
Inputs:
- Conversion Type (Triglycerides to VLDL or VLDL to Triglycerides)
- Value (Triglycerides or VLDL in mg/dL or mmol/L)
Health Status Thresholds for TG:
- mg/dL: Normal: ≤ 150; Elevated: 151–400; High: > 400
- mmol/L: Normal: ≤ 1.69; Elevated: 1.70–4.51; High: > 4.51
Steps:
- Select the conversion type (Triglycerides to VLDL or VLDL to Triglycerides).
- Input the value (Triglycerides or VLDL) and select its unit (mg/dL or mmol/L).
- The calculator converts the input to mg/dL for calculation, computes the converted value, and converts the result back to the input unit.
- Review the health status message based on the Triglycerides level.
3. Importance of VLDL and TG Conversion
Converting between VLDL and TG is useful for:
- Lipid Profile Assessment: VLDL and TG levels are related to cardiovascular risk, as high levels are associated with atherosclerosis.
- Health Monitoring: Helps track lipid levels to guide lifestyle changes or medical interventions to reduce cardiovascular risk.
- Clinical Decision-Making: Provides a simple estimate of VLDL or TG, aiding in the evaluation of lipid health when only one value is available.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Triglycerides 150 mg/dL (Input Unit: mg/dL, TG to VLDL):
VLDL: \( \frac{150}{5} = 30.00 \, \text{mg/dL} \).
Health Message: "Your Triglycerides level is normal (≤ 150 mg/dL)."
- VLDL 1.00 mmol/L (Input Unit: mmol/L, VLDL to TG):
TG: \( \frac{1.00}{0.166} \approx 6.02 \, \text{mmol/L} \).
Health Message: "Your Triglycerides level is high (> 4.51 mmol/L). This indicates an increased risk of cardiovascular issues. Please consult your healthcare provider."
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is VLDL?
A: Very Low-Density Lipoprotein (VLDL) is a type of lipoprotein that primarily transports triglycerides in the blood. High levels are associated with increased cardiovascular risk.
Q: Why are there different equations for high TG levels?
A: The Friedewald equation (\( \text{VLDL} = \frac{\text{TG}}{5} \)) is accurate for TG levels up to 400 mg/dL. For higher levels, the Wilson et al. equation (\( \text{VLDL} = \text{TG} \times 0.166 \)) accounts for hyperlipidemia and provides a more accurate estimate.
Q: How can I lower my TG and VLDL levels?
A: To lower TG and VLDL, reduce intake of sugars and refined carbohydrates, increase omega-3 fatty acids, maintain a healthy weight, exercise regularly, and limit alcohol consumption. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice or medication if needed.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back