1. What is the Stroke Volume Calculator?
Definition: The Stroke Volume Calculator estimates the volume of blood pumped by the heart per beat (Stroke Volume, SV), along with related indices such as Body Surface Area (BSA), Cardiac Index (CI), and Stroke Volume Index (SVI).
Purpose: It helps clinicians assess cardiac function and efficiency, providing insights into the heart’s ability to meet the body’s circulatory demands, particularly in conditions like heart failure or during exercise.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
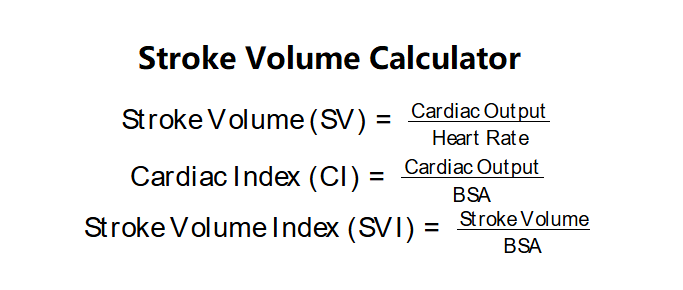
\( \text{Stroke Volume (SV)} = \frac{\text{Cardiac Output}}{\text{Heart Rate}} \)
\( \text{Body Surface Area (BSA)} = 0.007184 \times \text{Weight}^{0.425} \times \text{Height}^{0.725} \)
\( \text{Cardiac Index (CI)} = \frac{\text{Cardiac Output}}{\text{BSA}} \)
\( \text{Stroke Volume Index (SVI)} = \frac{\text{Stroke Volume}}{\text{BSA}} \)
Interpretation of Results:
- Stroke Volume (SV):
- <60 mL/beat: Low
- 60–120 mL/beat: Normal
- >120 mL/beat: High (common in athletes)
- Cardiac Index (CI):
- <2.5 L/min/m²: Low
- 2.5–4.0 L/min/m²: Normal
- >4.0 L/min/m²: High
- Stroke Volume Index (SVI):
- <35 mL/m²/beat: Low
- 35–60 mL/m²/beat: Normal
- >60 mL/m²/beat: High (common in athletes)
Inputs:
- Cardiac Output (L/min)
- Heart Rate (bpm)
- Height (cm)
- Weight (kg)
Steps:
- Input the patient’s cardiac output, heart rate, height, and weight.
- Calculate Stroke Volume, Body Surface Area, Cardiac Index, and Stroke Volume Index.
- Interpret the results based on standard ranges and provide a recommended action.
3. Importance of Stroke Volume Calculations
The Stroke Volume calculation is useful for:
- Assessing Cardiac Function: Stroke Volume and related indices like SVI and CI provide insights into the heart’s pumping efficiency.
- Diagnosing Heart Conditions: Low values may indicate heart failure, while high values in non-athletes may suggest hypervolemia or other conditions.
- Monitoring Exercise Physiology: Helps evaluate cardiovascular response in athletes, where high stroke volumes are common due to training adaptations.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Cardiac Output: 5 L/min, Heart Rate: 70 bpm, Height: 170 cm, Weight: 70 kg:
Stroke Volume: \( \frac{5 \times 1000}{70} \approx 71.43 \) mL/beat.
BSA: \( 0.007184 \times 70^{0.425} \times 170^{0.725} \approx 1.84 \) m².
Cardiac Index: \( \frac{5}{1.84} \approx 2.72 \) L/min/m².
Stroke Volume Index: \( \frac{71.43}{1.84} \approx 38.82 \) mL/m²/beat.
Interpretation: SV: Normal, CI: Normal, SVI: Normal.
Recommended Action: Normal values; continue regular monitoring.
- Cardiac Output: 8 L/min, Heart Rate: 50 bpm, Height: 180 cm, Weight: 80 kg:
Stroke Volume: \( \frac{8 \times 1000}{50} = 160 \) mL/beat.
BSA: \( 0.007184 \times 80^{0.425} \times 180^{0.725} \approx 2.01 \) m².
Cardiac Index: \( \frac{8}{2.01} \approx 3.98 \) L/min/m².
Stroke Volume Index: \( \frac{160}{2.01} \approx 79.60 \) mL/m²/beat.
Interpretation: SV: High, CI: Normal, SVI: High.
Recommended Action: High stroke volume and SVI; common in athletes. If not an athlete, evaluate for underlying causes.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is Stroke Volume?
A: Stroke Volume (SV) is the amount of blood pumped by the heart per beat, calculated as Cardiac Output divided by Heart Rate.
Q: Why calculate Stroke Volume Index?
A: Stroke Volume Index (SVI) normalizes stroke volume for body size (using BSA), allowing comparison across individuals with different body types.
Q: What does a high stroke volume indicate?
A: A high stroke volume (>120 mL/beat) is common in athletes due to enhanced cardiac efficiency. In non-athletes, it may suggest conditions like bradycardia, hypervolemia, or other cardiovascular abnormalities.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back