1. What is a Sodium in Salt Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the amount of sodium and pure salt (NaCl) in a given amount of salt, based on the type of salt and its quantity.
Purpose: It helps users monitor their sodium intake for dietary or health purposes and understand the pure salt content in their chosen salt type.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator takes the type of salt and the amount of salt with selectable units, and computes the sodium content and pure salt (NaCl) content using the following data and formulas:
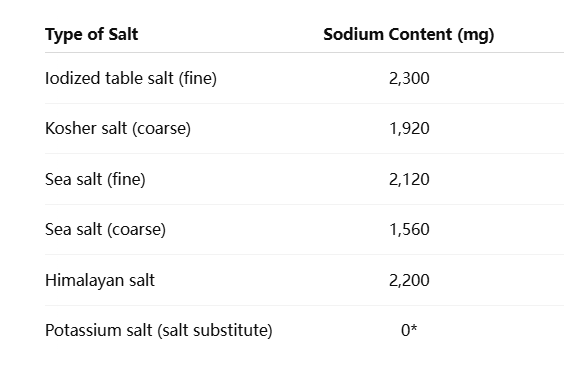
- Sodium Content per Teaspoon (tsp):
- Iodized Table Salt, Fine: 2,300 mg
- Kosher Salt, Coarse: 1,920 mg
- Sea Salt, Fine: 2,120 mg
- Sea Salt, Coarse: 1,560 mg
- Himalayan Salt: 2,200 mg
- Potassium Salt (Salt Substitute): 0 mg
- Sodium Calculation:
- \( \text{Sodium (mg)} = \text{Sodium per tsp (mg)} \times \text{Amount (tsp)} \)
- Pure Salt (NaCl) Calculation:
- \( \text{Pure Salt (mg)} = \text{Sodium (mg)} / 0.4 \)
- (Since sodium is approximately 40% of pure salt by weight, due to the atomic weights of sodium (23.00 u) and chlorine (35.34 u) in NaCl)
Unit Conversions:
- Salt Amount: tsp, g, cups (1 tsp = 5.69 g, 1 cup = 48 tsp).
- Sodium: mg, g, oz (1 g = 1,000 mg, 1 oz = 28,349.5 mg).
- Pure Salt: mg, g, kg, oz (1 g = 1,000 mg, 1 kg = 1,000,000 mg, 1 oz = 28,349.5 mg).
Steps:
- Select the type of salt.
- Input the amount of salt with chosen units.
- Compute the sodium and pure salt content.
- Adjust the output units using the dropdown menus.
3. Importance of Sodium in Salt Calculations
Calculating sodium in salt is useful for:
- Dietary Monitoring: Helps track sodium intake, which is crucial for managing blood pressure and heart health.
- Health Management: Assists in choosing lower-sodium salt options for those on restricted diets.
- Culinary Precision: Provides insight into the actual salt content for recipes, especially when substituting different types of salt.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Iodized Table Salt, Fine, 0.5 tsp:
Sodium: \( 2,300 \times 0.5 = 1,150.00 \, \text{mg} \).
Sodium in g: \( 1,150.00 / 1,000 = 1.1500 \, \text{g} \).
Sodium in oz: \( 1,150.00 / 28,349.5 \approx 0.0406 \, \text{oz} \).
Pure Salt: \( 1,150.00 / 0.4 = 2,875.00 \, \text{mg} \).
Pure Salt in g: \( 2,875.00 / 1,000 = 2.8750 \, \text{g} \).
Pure Salt in kg: \( 2,875.00 / 1,000,000 = 0.002875 \, \text{kg} \).
Pure Salt in oz: \( 2,875.00 / 28,349.5 \approx 0.1014 \, \text{oz} \).
- Sea Salt, Coarse, 2 g:
Amount in tsp: \( 2 / 5.69 \approx 0.3515 \, \text{tsp} \).
Sodium: \( 1,560 \times 0.3515 \approx 548.34 \, \text{mg} \).
Sodium in g: \( 548.34 / 1,000 \approx 0.5483 \, \text{g} \).
Sodium in oz: \( 548.34 / 28,349.5 \approx 0.0193 \, \text{oz} \).
Pure Salt: \( 548.34 / 0.4 \approx 1,370.85 \, \text{mg} \).
Pure Salt in g: \( 1,370.85 / 1,000 \approx 1.3709 \, \text{g} \).
Pure Salt in kg: \( 1,370.85 / 1,000,000 \approx 0.001371 \, \text{kg} \).
Pure Salt in oz: \( 1,370.85 / 28,349.5 \approx 0.0484 \, \text{oz} \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why does sodium content vary between salt types?
A: Sodium content varies due to differences in density and purity. Fine salts are denser, containing more sodium per tsp, while coarse salts have less. Potassium salt substitutes contain no sodium.
Q: How is pure salt (NaCl) calculated?
A: Pure salt is calculated by dividing the sodium content by 0.4, as sodium constitutes approximately 40% of NaCl by weight due to the atomic weights of sodium (23.00 u) and chlorine (35.34 u).
Q: Which salt has the least sodium?
A: Potassium salt (salt substitute) has 0 mg of sodium per tsp, making it the best option for a low-sodium diet. Among sodium-containing salts, sea salt (coarse) has the least at 1,560 mg per tsp.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back