1. What is the QTc Calculator?
Definition: The QTc Calculator corrects the QT interval for heart rate, providing the corrected QT interval (QTc) to assess the risk of arrhythmias.
Purpose: It helps clinicians identify patients at risk of life-threatening arrhythmias, such as torsades de pointes, often due to prolonged QTc intervals.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
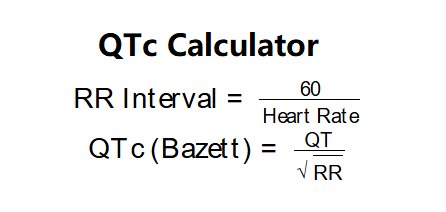
The calculator uses the following formulas:
\( \text{RR Interval} = \frac{60}{\text{Heart Rate}} \)
\( \text{QTc (Bazett)} = \frac{\text{QT}}{\sqrt{\text{RR}}} \)
Interpretation of QTc (ms) is sex-specific:
- Men:
- Normal: <430 ms
- Borderline: 430–450 ms
- Prolonged: >450 ms
- Women:
- Normal: <450 ms
- Borderline: 450–470 ms
- Prolonged: >470 ms
Inputs:
- Sex (Male/Female)
- QT Interval (ms)
- Heart Rate (bpm)
Steps:
- Input the patient’s sex, QT interval, and heart rate.
- Calculate the RR interval using RR = 60 / Heart Rate (in seconds).
- Compute QTc using Bazett’s formula.
- Interpret the QTc value based on sex-specific thresholds and provide a recommended action.
3. Importance of QTc Calculations
The QTc calculation is useful for:
- Risk Assessment: Prolonged QTc is associated with an increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias, such as torsades de pointes.
- Medication Safety: Helps identify patients at risk when starting QT-prolonging drugs (e.g., antiarrhythmics, antipsychotics).
- Monitoring Cardiac Health: Useful in conditions like electrolyte imbalances, congenital long QT syndrome, or drug toxicity.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Sex: Male, QT Interval: 400 ms, Heart Rate: 60 bpm:
RR Interval: \( \frac{60}{60} = 1 \) s.
QTc (Bazett): \( \frac{400}{\sqrt{1}} = 400 \) ms.
Interpretation: Normal.
Recommended Action: No increased risk of arrhythmias; continue regular monitoring.
- Sex: Female, QT Interval: 420 ms, Heart Rate: 80 bpm:
RR Interval: \( \frac{60}{80} = 0.75 \) s.
QTc (Bazett): \( \frac{420}{\sqrt{0.75}} \approx 485.24 \) ms.
Interpretation: Prolonged.
Recommended Action: High risk of arrhythmias; urgent evaluation needed.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is QTc?
A: QTc is the corrected QT interval, adjusted for heart rate, to assess the risk of arrhythmias. It’s typically calculated using Bazett’s formula: QTc = QT / √(RR).
Q: Why is QTc important?
A: A prolonged QTc can indicate a risk of life-threatening arrhythmias, such as torsades de pointes, often due to medications, electrolyte imbalances, or genetic conditions.
Q: What factors can prolong QTc?
A: Common factors include certain medications (e.g., antiarrhythmics, antipsychotics), electrolyte imbalances (e.g., low potassium or magnesium), hypothermia, and congenital long QT syndrome.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back