1. What is a Protein-to-Creatinine Ratio (PCR) Calculator?
Definition: The Protein-to-Creatinine Ratio (PCR) Calculator measures the ratio of protein to creatinine in a spot urine sample, providing an estimate of 24-hour urinary protein excretion.
Purpose: It helps clinicians assess proteinuria to diagnose and monitor kidney conditions like nephrotic syndrome or chronic kidney disease, offering a convenient alternative to 24-hour urine collection.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
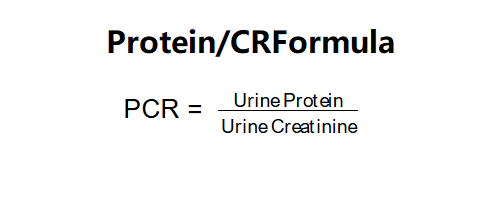
The calculator uses the following formula:
Unit Conversions (if needed):
- Urine Creatinine: 1 µmol/L = 0.0113 mg/dL
Steps:
- Input Urine Protein (mg/dL) and Urine Creatinine (mg/dL or µmol/L).
- Validate inputs (both values must be greater than zero).
- Convert Urine Creatinine to mg/dL if provided in µmol/L.
- Calculate the PCR by dividing Urine Protein by Urine Creatinine.
- Estimate 24-hour protein excretion by multiplying PCR by 1000 (to convert to mg/g).
- Display both the PCR (unitless) and the estimated 24-hour protein excretion (mg/g), rounded to 2 decimal places.
3. Importance of PCR Calculations
Calculating PCR is important for:
- Diagnosing Proteinuria: A PCR > 150 mg/g may indicate significant proteinuria, often associated with kidney damage or disease.
- Monitoring Kidney Disease: Helps track progression of conditions like diabetic nephropathy or glomerulonephritis without requiring a 24-hour urine collection.
- Guiding Treatment: Assists in determining the need for interventions, such as ACE inhibitors, to reduce proteinuria and protect kidney function.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: Urine Protein: 30 mg/dL, Urine Creatinine: 100 mg/dL
- PCR: \( \frac{30}{100} = 0.30 \)
- Estimated 24-Hour Protein Excretion: \( 0.30 \times 1000 = 300.00 \text{ mg/g} \)
- Example 2: Urine Protein: 50 mg/dL, Urine Creatinine: 4420 µmol/L
- Convert Urine Creatinine: \( 4420 \times 0.0113 = 50.00 \text{ mg/dL} \)
- PCR: \( \frac{50}{50} = 1.00 \)
- Estimated 24-Hour Protein Excretion: \( 1.00 \times 1000 = 1000.00 \text{ mg/g} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does a high PCR indicate?
A: A PCR > 150 mg/g suggests significant proteinuria, potentially indicating kidney damage such as nephrotic syndrome or glomerulonephritis.
Q: How does PCR compare to a 24-hour urine collection?
A: PCR is a convenient estimate of 24-hour protein excretion; while less accurate, it's easier to collect and sufficient for most clinical purposes.
Q: Can PCR be used in all patients?
A: PCR may be less reliable in patients with rapidly changing creatinine levels or muscle mass (e.g., in acute kidney injury or extremes of body weight)—consult a healthcare provider.
Protein-to-Creatinine Ratio (PCR) Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back