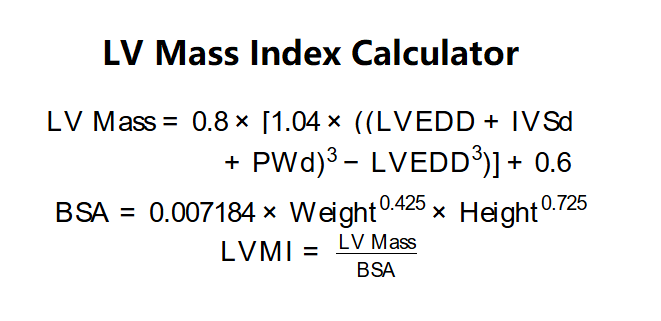1. What is the LV Mass Index Calculator?
Definition: The LV Mass Index Calculator estimates the Left Ventricular Mass (LV Mass) and Left Ventricular Mass Index (LVMI), which are indicators of heart muscle hypertrophy.
Purpose: It helps clinicians assess the presence and severity of left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), which is often associated with conditions like hypertension or aortic stenosis.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
\( \text{LV Mass} = 0.8 \times [1.04 \times ((\text{LVEDD} + \text{IVSd} + \text{PWd})^3 - \text{LVEDD}^3)] + 0.6 \)
\( \text{BSA} = 0.007184 \times \text{Weight}^{0.425} \times \text{Height}^{0.725} \)
\( \text{LVMI} = \frac{\text{LV Mass}}{\text{BSA}} \)
Interpretation of LVMI (g/m²) is based on sex-specific thresholds:
- Female: Normal: ≤95; Mild: 96–108; Moderate: 109–121; Severe: >121
- Male: Normal: ≤115; Mild: 116–131; Moderate: 132–148; Severe: >148
Inputs:
- Sex (Female/Male)
- Height (cm/m/in/ft)
- Weight (kg/oz/lb)
- LVEDD (Left Ventricular End-Diastolic Dimension, mm/cm/in)
- IVSd (Interventricular Septal End-Diastole, mm/cm/in)
- PWd (Posterior Wall Thickness at End-Diastole, mm/cm/in)
- Output Units: BSA (cm²/m²/in²/ft²), LV Mass (g/kg/oz/lb), LVMI (g/m²/g/in²/g/ft²)
Steps:
- Input the patient’s sex, height, weight, LVEDD, IVSd, PWd, and select units.
- Convert height and weight to cm and kg, and LVEDD, IVSd, PWd to cm for calculation.
- Calculate the Body Surface Area (BSA) using the Du Bois formula.
- Compute the Left Ventricular Mass (LV Mass) using the provided formula.
- Calculate the LVMI by dividing LV Mass by BSA.
- Convert results to the selected units and round to four decimal places.
- Interpret the LVMI (in g/m²) based on sex-specific thresholds and provide a recommended action.
3. Importance of LV Mass Index Calculations
The LV Mass Index calculation is useful for:
- Diagnosing LVH: Identifies left ventricular hypertrophy, a risk factor for cardiovascular events.
- Risk Assessment: Higher LVMI values are associated with increased risk of heart failure and arrhythmias.
- Guiding Treatment: Helps determine the need for interventions to manage underlying conditions like hypertension.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Sex: Male, Height: 5.58 ft, Weight: 154 lb, LVEDD: 50 mm, IVSd: 10 mm, PWd: 10 mm, BSA Unit: m², LV Mass Unit: g, LVMI Unit: g/m²:
Height: \( 5.58 \times 30.48 = 170.0784 \) cm.
Weight: \( 154 \div 2.20462 = 69.8532 \) kg.
LVEDD: \( 50 \times 0.1 = 5 \) cm, IVSd: \( 10 \times 0.1 = 1 \) cm, PWd: \( 10 \times 0.1 = 1 \) cm.
BSA: \( 0.007184 \times 69.8532^{0.425} \times 170.0784^{0.725} \approx 1.8389 \) m².
LV Mass: \( 0.8 \times [1.04 \times ((5 + 1 + 1)^3 - 5^3)] + 0.6 \approx 161.2000 \) g.
LVMI: \( \frac{161.2000}{1.8389} \approx 87.6457 \) g/m².
Interpretation: Normal.
Recommended Action: No action needed; continue regular monitoring.
- Sex: Female, Height: 160 cm, Weight: 2116.44 oz, LVEDD: 2.165 in, IVSd: 0.591 in, PWd: 0.591 in, BSA Unit: in², LV Mass Unit: lb, LVMI Unit: g/ft²:
Weight: \( 2116.44 \div 35.274 = 60.0000 \) kg.
LVEDD: \( 2.165 \times 2.54 = 5.4991 \) cm, IVSd: \( 0.591 \times 2.54 = 1.5011 \) cm, PWd: \( 0.591 \times 2.54 = 1.5011 \) cm.
BSA: \( 0.007184 \times 60^{0.425} \times 160^{0.725} \approx 1.6268 \) m² = \( 1.6268 \times 1550 = 2521.5400 \) in².
LV Mass: \( 0.8 \times [1.04 \times ((5.4991 + 1.5011 + 1.5011)^3 - 5.4991^3)] + 0.6 \approx 253.7657 \) g = \( 253.7657 \times 0.00220462 = 0.5594 \) lb.
LVMI: \( \frac{253.7657}{1.6268} \approx 155.9775 \) g/m² = \( \frac{155.9775}{10.764} \approx 14.4936 \) g/ft².
Interpretation: Severe hypertrophy.
Recommended Action: Urgent cardiology consultation; evaluate for advanced therapies.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the LV Mass Index?
A: LVMI is the left ventricular mass normalized by body surface area, used to assess for left ventricular hypertrophy.
Q: Why is sex important in LVMI interpretation?
A: Males and females have different normal ranges for LVMI due to physiological differences in heart size and body composition.
Q: What does a high LVMI indicate?
A: A high LVMI indicates left ventricular hypertrophy, which may be due to conditions like hypertension or aortic stenosis, increasing cardiovascular risk.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back