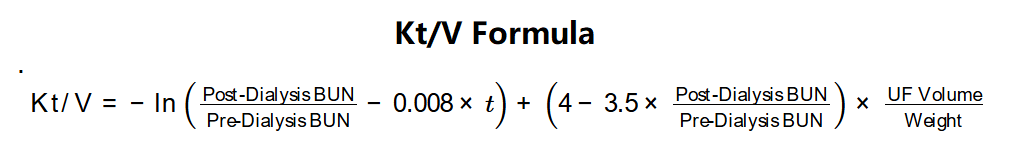1. What is a Kt/V Calculator?
Definition: The Kt/V Calculator measures dialysis adequacy in hemodialysis patients, where K is the dialyzer clearance of urea, t is dialysis time, and V is the patient's volume of distribution of urea (approximately total body water).
Purpose: It helps clinicians determine if a patient is receiving sufficient dialysis to remove waste products, ensuring optimal treatment and reducing complications.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the Daugirdas II formula:
Unit Conversions (if needed):
- BUN (Pre- and Post-Dialysis): 1 mmol/L = 2.8 mg/dL
- Weight: 1 lb = 0.453592 kg
Steps:
- Input Pre-Dialysis BUN (mg/dL or mmol/L), Post-Dialysis BUN (mg/dL or mmol/L), Dialysis Time (hours, defaults to 4), Ultrafiltration Volume (liters), and Post-Dialysis Weight (kg or lbs).
- Validate inputs (BUN values, dialysis time, and weight must be greater than zero; Post-Dialysis BUN must be less than Pre-Dialysis BUN; UF Volume cannot be negative).
- Convert Pre- and Post-Dialysis BUN to mg/dL if provided in mmol/L.
- Convert Post-Dialysis Weight to kg if provided in lbs.
- Calculate Kt/V using the Daugirdas II formula.
- Display the result, rounded to 2 decimal places.
3. Importance of Kt/V Calculations
Calculating Kt/V is important for:
- Assessing Dialysis Adequacy: A Kt/V ≥ 1.2 (for thrice-weekly dialysis) indicates adequate dialysis, reducing the risk of uremic complications.
- Optimizing Treatment: Helps adjust dialysis frequency, duration, or dialyzer settings to improve patient outcomes.
- Monitoring Patient Health: Ensures patients on hemodialysis maintain sufficient waste removal, improving quality of life and survival.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: Pre-Dialysis BUN: 70 mg/dL, Post-Dialysis BUN: 20 mg/dL, Dialysis Time: 4 hours, UF Volume: 3 liters, Post-Dialysis Weight: 70 kg
- BUN Ratio: \( \frac{20}{70} = 0.2857 \)
- First Term: \( -\ln(0.2857 - 0.008 \times 4) = -\ln(0.2537) = 1.3715 \)
- Second Term: \( \left(4 - 3.5 \times 0.2857\right) \times \frac{3}{70} = (4 - 1.0000) \times 0.0429 = 3.0000 \times 0.0429 = 0.1286 \)
- Kt/V: \( 1.3715 + 0.1286 = 1.50 \)
- Example 2: Pre-Dialysis BUN: 25 mmol/L, Post-Dialysis BUN: 7.14 mmol/L, Dialysis Time: 3.5 hours, UF Volume: 2 liters, Post-Dialysis Weight: 150 lbs
- Convert Pre-Dialysis BUN: \( 25 \times 2.8 = 70 \text{ mg/dL} \)
- Convert Post-Dialysis BUN: \( 7.14 \times 2.8 = 20.00 \text{ mg/dL} \)
- Convert Weight: \( 150 \times 0.453592 = 68.04 \text{ kg} \)
- BUN Ratio: \( \frac{20}{70} = 0.2857 \)
- First Term: \( -\ln(0.2857 - 0.008 \times 3.5) = -\ln(0.2577) = 1.3560 \)
- Second Term: \( \left(4 - 3.5 \times 0.2857\right) \times \frac{2}{68.04} = 3.0000 \times 0.0294 = 0.0882 \)
- Kt/V: \( 1.3560 + 0.0882 = 1.44 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does a low Kt/V indicate?
A: A Kt/V < 1.2 suggests inadequate dialysis, which may lead to uremic symptoms, fluid overload, or other complications.
Q: How often should Kt/V be measured?
A: Typically monthly for stable hemodialysis patients, or more frequently if dialysis parameters change—consult a healthcare provider.
Q: Can Kt/V be used for peritoneal dialysis?
A: This calculator uses the Daugirdas II formula for hemodialysis; peritoneal dialysis requires a different Kt/V calculation method.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back