1. What is a Harris-Benedict BMR Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) using the Harris-Benedict equation, and your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) by factoring in your physical activity level (PAL).
Purpose: It helps estimate the number of calories your body needs at rest (BMR) and throughout the day (TDEE), useful for nutritional planning, weight management, or fitness goals.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator takes sex, age, height, weight, and physical activity level with selectable units and computes:
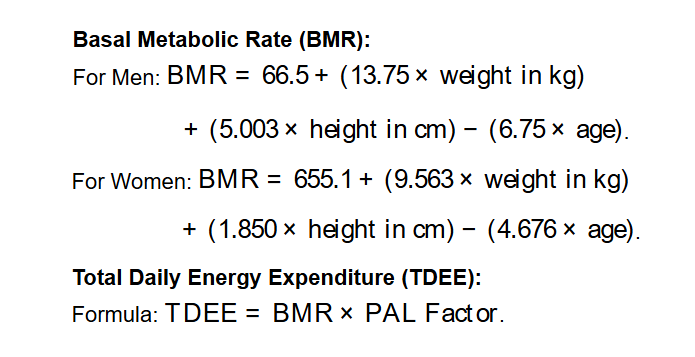
- Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR):
- For Men: \( \text{BMR} = 66.5 + (13.75 \times \text{weight in kg}) + (5.003 \times \text{height in cm}) - (6.75 \times \text{age}) \).
- For Women: \( \text{BMR} = 655.1 + (9.563 \times \text{weight in kg}) + (1.850 \times \text{height in cm}) - (4.676 \times \text{age}) \).
- Result in kcal/day.
- Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE):
- Formula: \( \text{TDEE} = \text{BMR} \times \text{PAL Factor} \).
- PAL Factors: Sedentary (1.2), Lightly active (1.375), Moderately active (1.55), Very active (1.725), Extra active (1.9), Professional athlete (2.3).
- Result in kcal/day.
Unit Conversions:
- Height: cm, m, in, ft (e.g., 1 m = 100 cm = 39.3701 in).
- Weight: kg, lb, oz (e.g., 1 kg = 2.20462 lb).
Steps:
- Select your sex.
- Input your age (in years), height, and weight with chosen units.
- Select your physical activity level (PAL).
- Compute your BMR and TDEE.
3. Importance of BMR and TDEE Calculations
Calculating BMR and TDEE is useful for:
- Nutritional Planning: Determines calorie needs for maintaining, gaining, or losing weight, tailored to your activity level.
- Weight Management: Helps set calorie goals based on your energy expenditure, supporting weight loss or gain strategies.
- Fitness Goals: Provides a baseline for athletes or active individuals to optimize performance and recovery through proper nutrition.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Male, Age 30: Height = 180 cm, Weight = 70 kg, PAL = Moderately active (1.55)
BMR: \( 66.5 + (13.75 \times 70) + (5.003 \times 180) - (6.75 \times 30) \approx 1726.04 \, \text{kcal/day} \).
TDEE: \( 1726.04 \times 1.55 \approx 2675.36 \, \text{kcal/day} \).
- Female, Age 25: Height = 65 in (165.1 cm), Weight = 130 lb (58.97 kg), PAL = Very active (1.725)
BMR: \( 655.1 + (9.563 \times 58.97) + (1.850 \times 165.1) - (4.676 \times 25) \approx 1407.64 \, \text{kcal/day} \).
TDEE: \( 1407.64 \times 1.725 \approx 2428.18 \, \text{kcal/day} \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does BMR represent?
A: BMR represents the number of calories your body needs at rest to maintain basic functions like breathing, circulation, and cell production, measured in kcal/day.
Q: What does TDEE include?
A: TDEE includes your BMR adjusted for your physical activity level (PAL), providing an estimate of the total calories you burn daily, including exercise and daily activities.
Q: How do I choose the right PAL?
A: Choose your PAL based on your weekly activity: Sedentary for little exercise, Lightly active for light exercise 1–3 days, Moderately active for moderate exercise 3–5 days, Very active for hard exercise 6–7 days, Extra active for very hard exercise and a physical job, or Professional athlete for elite training.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back