1. What is the Gorlin Formula Calculator?
Definition: The Gorlin Formula Calculator estimates the Aortic Valve Area (AVA) and approximates the Mitral Valve Area (MVA) using hemodynamic measurements from echocardiography or catheterization, with support for multiple unit conversions.
Purpose: It helps clinicians assess the severity of aortic and mitral valve stenosis, guiding decisions on interventions like valve replacement.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator computes AVA and MVA with unit conversion in the following steps:
- Convert Inputs:
- CO: Converted to mL/min (1 L/min = 1000 mL/min).
- ΔP: Converted to mmHg (1 kPa = 7.50062 mmHg).
- Aortic Valve Area (AVA):
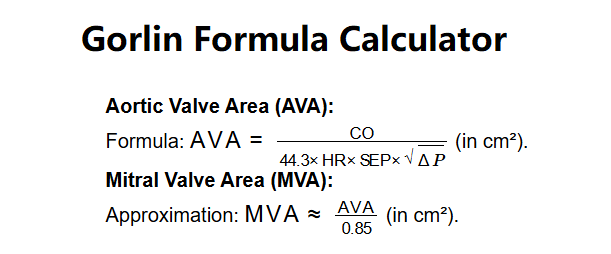
- Formula: \( \text{AVA} = \frac{\text{CO}}{44.3 \times \text{HR} \times \text{SEP} \times \sqrt{\Delta P}} \) (in cm²).
- Mitral Valve Area (MVA):
- Approximation: \( \text{MVA} \approx \frac{\text{AVA}}{0.85} \) (in cm²).
- Convert Outputs:
- AVA and MVA: Converted to selected units (e.g., 1 cm² = 100 mm², 1 cm² = 0.155 in²).
Steps:
- Input Cardiac Output (CO), Heart Rate (HR), Systolic Ejection Period (SEP), and Pressure Gradient (ΔP).
- Select units for inputs and desired output units for AVA and MVA.
- The calculator computes AVA and MVA, converts to the chosen units, and classifies the results in cm².
3. Importance of Gorlin Formula Calculations
The Gorlin Formula is crucial for:
- Diagnosis: Quantifies the severity of aortic and mitral valve stenosis, aiding in the diagnosis of conditions like aortic stenosis.
- Treatment Planning: Helps determine if surgical intervention (e.g., valve replacement) is necessary.
- Prognosis: Provides insights into the hemodynamic impact of valve stenosis on cardiac function.
Classification of Valve Areas
| Classification |
AVA (cm²) |
MVA (cm²) |
| Normal |
3–4 |
4–6 |
| Mild |
1.5–3 |
1.5–4 |
| Moderate |
1–1.5 |
1–1.5 |
| Severe |
< 1 |
< 1 |
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: CO = 5000 mL/min, HR = 70 beats/min, SEP = 0.3 sec/beat, ΔP = 40 mmHg, AVA unit = mm², MVA unit = in²
AVA: \( \frac{5000}{44.3 \times 70 \times 0.3 \times \sqrt{40}} \approx 0.84987 \, \text{cm}^2 = 84.98660 \, \text{mm}^2 \).
MVA: \( \frac{0.84987}{0.85} \approx 0.99985 \, \text{cm}^2 = 0.15498 \, \text{in}^2 \).
Classification: AVA: Severe (AVA = 0.84987 cm²), MVA: Severe (MVA = 0.99985 cm²).
Recommendation: Consider consulting a cardiologist for further evaluation and potential intervention.
- Example 2: CO = 6 L/min, HR = 80 beats/min, SEP = 0.25 sec/beat, ΔP = 4 kPa, AVA unit = in², MVA unit = cm²
Convert: CO = \( 6 \times 1000 = 6000 \, \text{mL/min} \), ΔP = \( 4 \times 7.50062 = 30.00248 \, \text{mmHg} \).
AVA: \( \frac{6000}{44.3 \times 80 \times 0.25 \times \sqrt{30.00248}} \approx 1.23580 \, \text{cm}^2 = 0.19155 \, \text{in}^2 \).
MVA: \( \frac{1.23580}{0.85} \approx 1.45388 \, \text{cm}^2 \).
Classification: AVA: Moderate (AVA = 1.23580 cm²), MVA: Moderate (MVA = 1.45388 cm²).
Recommendation: Consider consulting a cardiologist for further evaluation and potential intervention.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the Gorlin Formula used for?
A: It calculates the aortic valve area (AVA) to assess the severity of aortic stenosis and can approximate the mitral valve area (MVA) for mitral stenosis.
Q: How accurate is the MVA approximation?
A: The MVA approximation (AVA / 0.85) is empirical and provides a rough estimate. For precise MVA, consider using Doppler echocardiography or a PISA calculator.
Q: How does unit conversion work for the results?
A: AVA and MVA are calculated in cm², then converted to the selected units (e.g., 1 cm² = 100 mm², 1 cm² = 0.155 in²) for display.
Gorlin Formula Calculator with Unit Conversion© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back