1. What is an EROA Calculator?
Definition: The EROA Calculator determines the Effective Regurgitant Orifice Area (EROA) for mitral valve regurgitation using echocardiographic measurements. It requires the radius of the regurgitant orifice (r), the aliasing speed (Va), and the maximal velocity (Vmax), with support for multiple unit conversions.
Purpose: EROA is a key parameter in assessing the severity of mitral regurgitation, helping clinicians decide on treatment options such as surgery or medical management.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator computes EROA with unit conversion in the following steps:
- Convert Inputs:
- Radius (r): Converted to cm (e.g., 1 mm = 0.1 cm, 1 in = 2.54 cm).
- Velocities (Va, Vmax): Converted to cm/s (e.g., 1 mm/s = 0.1 cm/s, 1 in/s = 2.54 cm/s).
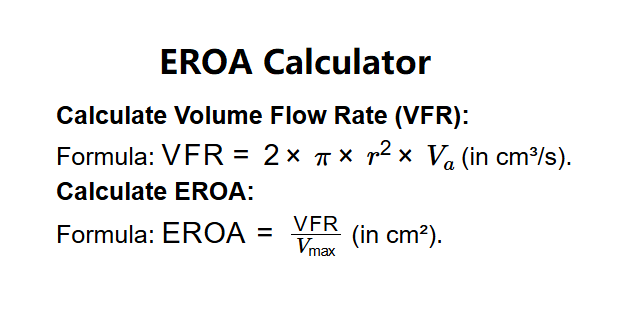
- Calculate Volume Flow Rate (VFR):
- Formula: \( \text{VFR} = 2 \times \pi \times r^2 \times V_a \) (in cm³/s).
- Calculate EROA:
- Formula: \( \text{EROA} = \frac{\text{VFR}}{V_{\text{max}}} \) (in cm²).
- Convert Outputs:
- VFR: Converted to selected unit (e.g., 1 cm³/s = 1000 mm³/s, 1 cm³/s = 0.0610237 in³/s).
- EROA: Converted to selected unit (e.g., 1 cm² = 100 mm², 1 cm² = 0.155 in²).
Steps:
- Obtain the radius (r), aliasing speed (Va), and maximal velocity (Vmax) from an echocardiogram.
- Select the units for each input and desired output units.
- Input the values and compute VFR and EROA in the chosen units.
3. Importance of EROA Calculations
Calculating EROA is crucial for:
- Severity Assessment: EROA quantifies the severity of mitral regurgitation. For example, an EROA ≥ 0.4 cm² indicates severe regurgitation.
- Treatment Decisions: Helps determine if a patient needs surgical intervention (e.g., mitral valve repair or replacement).
- Prognosis: Provides insight into the impact of regurgitation on cardiac function and patient outcomes.
Normal and Abnormal EROA Values
| EROA (cm²) |
Severity |
| < 0.2 |
Mild |
| 0.2–0.39 |
Moderate |
| ≥ 0.4 |
Severe |
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: Radius (r) = 5 mm, Aliasing Speed (Va) = 400 mm/s, Vmax = 5000 mm/s, VFR unit = ml/s, EROA unit = mm²
Convert: \( r = 5 \, \text{mm} = 0.5 \, \text{cm} \), \( V_a = 400 \, \text{mm/s} = 40 \, \text{cm/s} \), \( V_{\text{max}} = 5000 \, \text{mm/s} = 500 \, \text{cm/s} \).
VFR: \( 2 \times \pi \times (0.5)^2 \times 40 = 62.83 \, \text{cm}^3/\text{s} = 62.83 \, \text{ml/s} \).
EROA: \( \frac{62.83}{500} = 0.1257 \, \text{cm}^2 = 12.57 \, \text{mm}^2 \).
Interpretation: An EROA of 12.57 mm² (0.1257 cm²) indicates mild regurgitation.
- Example 2: Radius (r) = 0.7 cm, Aliasing Speed (Va) = 38 cm/s, Vmax = 400 cm/s, VFR unit = in³/s, EROA unit = in²
VFR: \( 2 \times \pi \times (0.7)^2 \times 38 = 116.87 \, \text{cm}^3/\text{s} = 7.13 \, \text{in}^3/\text{s} \).
EROA: \( \frac{116.87}{400} = 0.2922 \, \text{cm}^2 = 0.0453 \, \text{in}^2 \).
Interpretation: An EROA of 0.0453 in² (0.2922 cm²) indicates moderate regurgitation.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the aliasing speed (Va) in echocardiography?
A: Aliasing speed (Va) is the velocity at which color Doppler signals alias, typically measured at the proximal isovelocity surface area (PISA) during echocardiography.
Q: Why is EROA important for mitral regurgitation?
A: EROA quantifies the size of the regurgitant orifice, directly reflecting the severity of regurgitation and guiding clinical decisions.
Q: How does unit conversion work in this calculator?
A: The calculator converts all inputs to cm and cm/s for internal calculations, then converts the results (VFR and EROA) to the user-selected units using standard conversion factors (e.g., 1 cm = 10 mm, 1 cm² = 0.155 in²).
EROA Calculator with Unit Conversion© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back