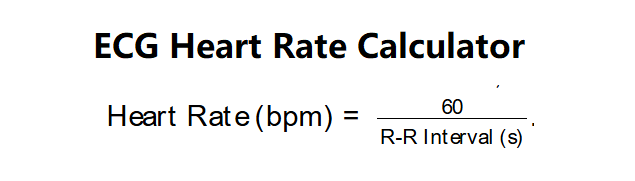1. What is an ECG Heart Rate Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the heart rate (in beats per minute, bpm) from an electrocardiogram (ECG) by measuring the R-R interval, the distance between two consecutive R waves. It requires inputs for the R-R interval (in millimeters or boxes), box type (if using boxes), and ECG paper speed.
Purpose: Calculating heart rate from an ECG helps clinicians assess cardiac rhythm, diagnose conditions like bradycardia or tachycardia, and monitor heart function. This calculator is designed for regular rhythms only.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator computes heart rate using the R-R interval:
- R-R Interval in Millimeters:
- Convert R-R interval to seconds: At 25 mm/s, 1 mm = 0.04 s; at 50 mm/s, 1 mm = 0.02 s.
- Formula: \( \text{Heart Rate (bpm)} = \frac{60}{\text{R-R Interval (s)}} \).
- R-R Interval in Boxes:
- Large box (5 mm): 0.2 s at 25 mm/s, 0.1 s at 50 mm/s.
- Small box (1 mm): 0.04 s at 25 mm/s, 0.02 s at 50 mm/s.
- Formula: \( \text{Heart Rate (bpm)} = \frac{60}{\text{R-R Interval (s)}} \).
Steps:
- Measure the R-R interval (distance between two consecutive R waves) on the ECG.
- Input the interval in millimeters or boxes, select box type if using boxes, and choose the paper speed.
- Compute the heart rate and view the classification and prompt.
3. Importance of ECG Heart Rate Calculations
Calculating heart rate from an ECG is useful for:
- Cardiac Assessment: Identifies bradycardia (<60 bpm) or tachycardia (>100 bpm), which may indicate underlying conditions.
- Monitoring: Tracks heart rate changes in clinical settings or during stress tests.
- Diagnosis: Helps diagnose arrhythmias when combined with rhythm analysis.
Heart Rate Classification (Adults)
| Heart Rate (bpm) |
Classification |
| < 60 |
Bradycardia |
| 60–100 |
Normal |
| > 100 |
Tachycardia |
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: R-R Interval = 15 mm, Paper Speed = 25 mm/s
Time per mm: 0.04 s.
R-R Interval: \( 15 \times 0.04 = 0.6 \, \text{s} \).
Heart Rate: \( \frac{60}{0.6} = 100.00 \, \text{bpm} \).
Classification: Normal.
Prompt: The heart rate is within the normal range for adults (60–100 bpm).
- Example 2: R-R Interval = 2 large boxes, Paper Speed = 25 mm/s
Time per large box: 0.2 s.
R-R Interval: \( 2 \times 0.2 = 0.4 \, \text{s} \).
Heart Rate: \( \frac{60}{0.4} = 150.00 \, \text{bpm} \).
Classification: Tachycardia.
Prompt: The heart rate is above normal, which may indicate tachycardia. Consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the R-R interval?
A: The R-R interval is the distance between two consecutive R waves on an ECG, representing the time between heartbeats.
Q: Why does paper speed matter?
A: Paper speed determines the time scale of the ECG. At 25 mm/s, 1 mm = 0.04 s; at 50 mm/s, 1 mm = 0.02 s, affecting the heart rate calculation.
Q: Can this calculator be used for irregular rhythms?
A: No, this calculator is designed for regular rhythms only. For irregular rhythms, other methods like the 6-second method are recommended.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back