1. What is an ECG Boxes to Seconds Calculator?
Definition: This calculator converts the number of boxes on an electrocardiogram (ECG) strip into a duration in seconds or milliseconds. It requires inputs for the number of boxes, the type of boxes (large or small), and the ECG paper speed.
Purpose: It helps clinicians and medical students determine the duration of ECG intervals or segments (e.g., PR interval, QRS complex, QT interval), which is crucial for diagnosing conditions like heart block or arrhythmias.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator computes the duration based on the number of boxes:
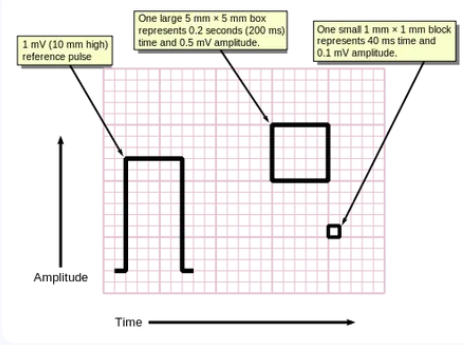
- Large Box (5 mm):
- At 25 mm/s: 1 large box = 0.2 s.
- At 50 mm/s: 1 large box = 0.1 s.
- Small Box (1 mm):
- At 25 mm/s: 1 small box = 0.04 s.
- At 50 mm/s: 1 small box = 0.02 s.
- Duration:
- Seconds: \( \text{Duration (s)} = \text{Number of Boxes} \times \text{Time per Box} \).
- Milliseconds: \( \text{Duration (ms)} = \text{Duration (s)} \times 1000 \).
Steps:
- Count the number of boxes between two points on the ECG (e.g., start of P wave to start of QRS for PR interval).
- Input the number of boxes, select the box type, and choose the paper speed.
- Compute the duration in seconds and milliseconds.
3. Importance of ECG Boxes to Seconds Calculations
Converting ECG boxes to seconds is useful for:
- Interval Measurement: Determines durations of ECG intervals (e.g., PR, QRS, QT), aiding in the diagnosis of conditions like first-degree heart block (prolonged PR interval).
- Cardiac Assessment: Helps identify abnormalities in electrical conduction that may indicate heart disease.
- Education: Assists medical students in learning ECG interpretation by providing precise time measurements.
Normal ECG Interval Values
| Interval |
Normal Duration (s) |
Normal Duration (ms) |
| PR Interval |
0.12–0.20 |
120–200 |
| QRS Complex |
0.06–0.12 |
60–120 |
| QT Interval |
0.36–0.44 (varies with heart rate) |
360–440 |
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: Number of Boxes = 4 large boxes, Paper Speed = 25 mm/s
Time per large box: 0.2 s.
Duration: \( 4 \times 0.2 = 0.8000 \, \text{s} = 800.00 \, \text{ms} \).
Interpretation: A PR interval of 0.8 s (800 ms) indicates a significant prolongation, possibly a first-degree heart block.
- Example 2: Number of Boxes = 10 small boxes, Paper Speed = 50 mm/s
Time per small box: 0.02 s.
Duration: \( 10 \times 0.02 = 0.2000 \, \text{s} = 200.00 \, \text{ms} \).
Interpretation: A PR interval of 0.2 s (200 ms) is within the normal range (120–200 ms).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between large and small boxes on an ECG?
A: A large box (5 mm) is made up of 5 small boxes (1 mm each). At 25 mm/s, a large box represents 0.2 s, and a small box represents 0.04 s; at 50 mm/s, these are 0.1 s and 0.02 s, respectively.
Q: Why does paper speed matter?
A: Paper speed affects the time scale of the ECG. At 25 mm/s, 1 mm = 0.04 s; at 50 mm/s, 1 mm = 0.02 s, which changes the duration calculation.
Q: How can this calculator help diagnose heart block?
A: By converting the PR interval to seconds, you can determine if it exceeds 0.2 s (200 ms), which may indicate a first-degree heart block.
ECG Boxes to Seconds Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back