 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: This calculator computes the CHA2DS2-VASc Score, a clinical tool used to assess the risk of stroke in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (AF). It considers seven risk factors: Congestive Heart Failure, Hypertension, Age, Diabetes, Stroke/TIA history, Vascular Disease, and Sex.
Purpose: The CHA2DS2-VASc Score helps clinicians determine the need for anticoagulation therapy to prevent stroke in AF patients, balancing the risk of thromboembolism against the risk of bleeding.
The calculator evaluates the following risk factors and assigns points:
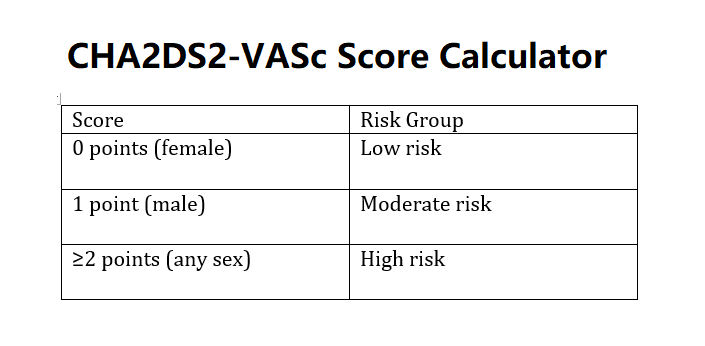
Total Score: The sum of points (0–9) indicates stroke risk.
Steps:
Calculating the CHA2DS2-VASc Score is useful for:
| Score | Risk Classification | Annual Stroke Risk (%) | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Low | 0.2 | No antithrombotic therapy |
| 1 | Low-Moderate | 0.6 | Consider antiplatelet or anticoagulation |
| 2 | Moderate-High | 2.2 | Oral anticoagulation recommended |
| 3 | Moderate-High | 3.2 | Oral anticoagulation recommended |
| 4 | High | 4.8 | Oral anticoagulation strongly recommended |
| 5 | High | 7.2 | Oral anticoagulation strongly recommended |
| 6 | High | 9.7 | Oral anticoagulation strongly recommended |
| 7 | High | 11.2 | Oral anticoagulation strongly recommended |
| 8–9 | High | 12.0–13.0 | Oral anticoagulation strongly recommended |
Examples:
Q: What does the CHA2DS2-VASc Score indicate?
A: It estimates the annual risk of stroke in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Higher scores indicate a greater risk, guiding anticoagulation decisions.
Q: How does CHA2DS2-VASc differ from CHADS2?
A: CHA2DS2-VASc includes additional risk factors (age 65–74, vascular disease, female sex) for better stratification, especially in low-risk patients.
Q: Should I also assess bleeding risk?
A: Yes, use the HAS-BLED score to evaluate bleeding risk before initiating anticoagulation therapy.