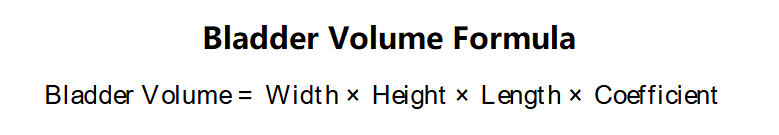1. What is a Bladder Volume Calculator?
Definition: The Bladder Volume Calculator estimates the volume of the bladder based on its shape and three-dimensional measurements, typically obtained via ultrasound.
Purpose: It helps clinicians assess bladder capacity, diagnose urinary retention, or monitor conditions like overactive bladder or neurogenic bladder dysfunction.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula for all shapes, adjusted by a shape-specific coefficient:
Unit Conversions (if needed):
- Dimensions: 1 inch = 2.54 cm
- Volume (from mL):
- 1 mL = 1000 mm³
- 1 mL = 1 cm³
- 1 mL = 0.000001 m³
- 1 mL = 0.0610237 in³
- 1 mL = 0.0000353147 ft³
- 1 mL = 0.0000013080 yd³
- 1 mL = 0.001 L
Steps:
- Select the bladder shape (Ellipsoid, Cuboid, Triangular Prism, Prolate Ellipsoid, or Custom).
- If Custom is selected, input the coefficient (default is 0.7).
- Input the three dimensions (Width, Height, Length), selecting the unit for each (cm or inches).
- Select the output volume unit (mm³, cm³, m³, in³, ft³, yd³, or L).
- Validate inputs (all dimensions and the custom coefficient must be greater than zero).
- Convert each dimension to cm if provided in inches.
- Calculate the base volume in mL using Width × Height × Length.
- Apply the shape-specific coefficient to get the final volume in mL.
- Convert the volume to the selected output unit.
- Display the result with the unit dropdown, rounded to 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Bladder Volume Calculations
Calculating bladder volume is important for:
- Diagnosing Urinary Issues: Helps identify conditions like urinary retention or incomplete bladder emptying.
- Monitoring Bladder Health: Useful in managing patients with bladder dysfunction due to neurological conditions or post-surgery.
- Guiding Treatment: Assists in determining the need for interventions like catheterization or medication adjustments.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: Shape: Ellipsoid, Width: 10 cm, Height: 8 cm, Length: 6 cm, Output: cm³
- Base Volume: \( 10 \times 8 \times 6 = 480 \text{ mL} \)
- Apply Coefficient (0.81): \( 480 \times 0.81 = 388.8000 \text{ mL} \)
- Convert to cm³ (same as mL): \( 388.8000 \text{ cm³} \)
- Example 2: Shape: Cuboid, Width: 4 inches, Height: 3 inches, Length: 2 inches, Output: L
- Convert Dimensions: \( 4 \times 2.54 = 10.16 \text{ cm}, 3 \times 2.54 = 7.62 \text{ cm}, 2 \times 2.54 = 5.08 \text{ cm} \)
- Base Volume in mL: \( 10.16 \times 7.62 \times 5.08 = 393.4746 \text{ mL} \)
- Apply Coefficient (0.89): \( 393.4746 \times 0.89 = 350.1924 \text{ mL} \)
- Convert to L: \( 350.1924 \times 0.001 = 0.3502 \text{ L} \)
- Example 3: Shape: Custom, Coefficient: 0.5, Width: 10 cm, Height: 8 cm, Length: 6 cm, Output: cm³
- Base Volume: \( 10 \times 8 \times 6 = 480 \text{ mL} \)
- Apply Coefficient (0.5): \( 480 \times 0.5 = 240.0000 \text{ mL} \)
- Convert to cm³ (same as mL): \( 240.0000 \text{ cm³} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why use different shapes for bladder volume?
A: Bladder shape varies between individuals; different models approximate common shapes, with coefficients adjusting for anatomical variations.
Q: How are bladder dimensions measured?
A: Typically via ultrasound, measuring width, height, and length of the bladder in three planes.
Q: What is a normal bladder volume?
A: Normal adult bladder capacity is typically 400–600 mL, but this varies; consult a healthcare provider for personalized assessment.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back