 Home
Home
 Back
Back
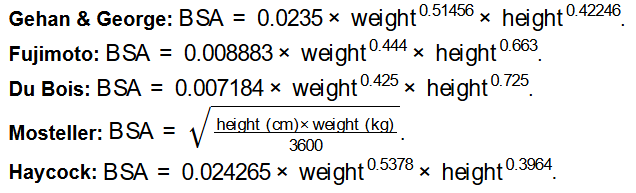
Definition: This calculator computes the Body Surface Area (BSA), a measure of the total surface area of a person's body, based on their height and weight. It supports multiple formulas (Gehan & George, Fujimoto, Du Bois, Mosteller, Haycock) to estimate BSA, which is typically expressed in square meters.
Purpose: BSA is used in medical and clinical settings to calculate medication dosages, assess metabolic rates, and evaluate physiological functions like cardiac output and renal clearance.
The calculator takes height and weight with selectable units and computes BSA using one of the following formulas:
Unit Conversions:
Steps:
Calculating BSA is useful for:
Examples:
Q: Why are there different formulas for BSA?
A: Different formulas were developed to improve accuracy across diverse populations and body types. For example, Mosteller is simpler and widely used, while Du Bois and Haycock may be more accurate for specific groups.
Q: How is BSA used in medicine?
A: BSA is used to calculate medication dosages, especially for drugs with narrow therapeutic ranges like chemotherapy agents, and to assess physiological functions like cardiac output and glomerular filtration rate.
Q: Why can I choose different units for measurements?
A: The calculator allows flexible unit selection for height, weight, and BSA to accommodate various measurement preferences, converting all inputs to standard units (cm, kg) for calculation and displaying results in your chosen unit.