1. What is the Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) Calculator?
Definition: The Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) Calculator computes the ratio of the systolic blood pressure at the ankle to the systolic blood pressure in the arm (brachial artery). It is a non-invasive test to assess peripheral artery disease (PAD).
Purpose: It helps diagnose and evaluate the severity of PAD, which can indicate blockages or narrowing in the arteries of the legs, often associated with cardiovascular risk.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas to compute the ABI for the selected leg:
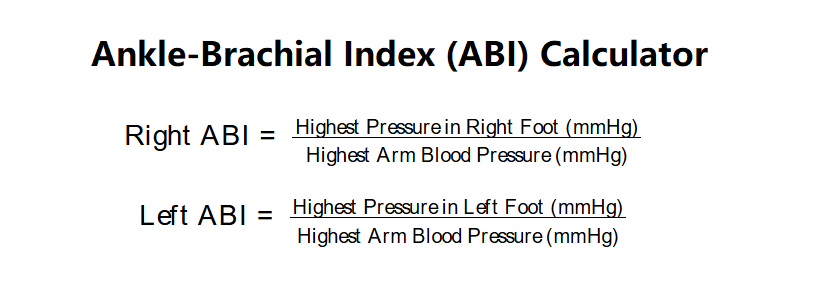
- Right ABI:
\( \text{Right ABI} = \frac{\text{Highest Pressure in Right Foot (mmHg)}}{\text{Highest Arm Blood Pressure (mmHg)}} \)
- Left ABI:
\( \text{Left ABI} = \frac{\text{Highest Pressure in Left Foot (mmHg)}}{\text{Highest Arm Blood Pressure (mmHg)}} \)
The interpretation is based on the calculated ABI value, with the following ranges:
- Above 1.4: Result indicates calcification or vessel hardening. (Consult a vascular specialist!)
- 1.0–1.4: Normal. (No action needed.)
- 0.9–1.0: Acceptable. (No action needed.)
- 0.8–0.9: Mild arterial disease might be present. (Consult your doctor about the result and treat risk factors according to their recommendations.)
- 0.5–0.8: Moderate arterial disease. (Consult a vascular specialist!)
- Below 0.5: Severe arterial disease. (Consult a vascular specialist!)
Inputs:
- Calculation Type (Right ABI or Left ABI)
- Highest Arm Blood Pressure (mmHg)
- Highest Pressure in Right Foot (mmHg, if calculating Right ABI)
- Highest Pressure in Left Foot (mmHg, if calculating Left ABI)
Steps:
- Select whether to calculate the Right ABI or Left ABI.
- Input the highest arm blood pressure (brachial systolic pressure).
- Input the highest pressure in the selected foot (right or left).
- Compute the selected ABI value by dividing the foot pressure by the arm pressure.
- Interpret the result and provide a recommended action.
3. Importance of ABI Calculations
The ABI calculation is useful for:
- Diagnosing PAD: Identifies peripheral artery disease by comparing blood pressure in the arms and legs.
- Risk Assessment: Indicates cardiovascular risk, as PAD is often associated with other vascular conditions.
- Guiding Treatment: Provides actionable insights for managing arterial disease, from monitoring to specialist consultation.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Calculate Right ABI, Highest Arm Blood Pressure: 130 mmHg, Highest Pressure in Right Foot: 120 mmHg:
Right ABI: \( \frac{120}{130} \approx 0.92 \).
Interpretation: Acceptable.
Recommended Action: No action needed.
- Calculate Left ABI, Highest Arm Blood Pressure: 100 mmHg, Highest Pressure in Left Foot: 140 mmHg:
Left ABI: \( \frac{140}{100} = 1.40 \).
Interpretation: Result indicates calcification or vessel hardening.
Recommended Action: Consult a vascular specialist!
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI)?
A: The ABI is a ratio of the systolic blood pressure at the ankle to the systolic blood pressure in the arm, used to diagnose peripheral artery disease (PAD).
Q: Why calculate only one side's ABI?
A: Calculating one side's ABI can be useful if you're assessing a specific leg for symptoms or monitoring a known condition on that side.
Q: What does a low ABI value mean?
A: An ABI below 0.9 indicates potential arterial disease, ranging from mild (0.8–0.9) to severe (below 0.5), and may require medical consultation.
Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back