1. What is a Traffic Density Calculator?
Definition: This calculator determines traffic flow, density, headway, and average travel speed based on the number of vehicles passing a point over time and the number of vehicles occupying a road segment.
Purpose: It helps traffic engineers and planners analyze traffic conditions, estimate travel speeds, and understand vehicle spacing on a road segment.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
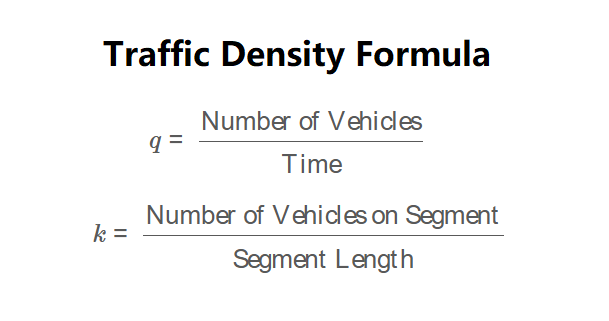
Flow (\( q \)):
\[
q = \frac{\text{Number of Vehicles}}{\text{Time}}
\]
Density (\( k \)):
\[
k = \frac{\text{Number of Vehicles on Segment}}{\text{Segment Length}}
\]
Headway (\( h \)):
\[
h = \frac{1}{k}
\]
Average Travel Speed (\( s \)):
\[
s = \frac{q}{k}
\]
Where:
- \( q \): Flow (vehicles/hour)
- \( k \): Density (vehicles/km)
- \( h \): Headway (meters)
- \( s \): Average travel speed (km/h, convertible to other units)
Unit Conversions:
- Time:
- 1 hour = 60 minutes
- 1 hour = 3600 seconds
- Length:
- 1 mile = 1.60934 km
- 1 km = 1000 m
- 1 km = 3280.84 ft
- Speed:
- 1 km/h = 0.621371 mph
- 1 km/h = 0.277778 m/s
- 1 km/h = 0.911344 ft/s
Steps:
- Enter the number of vehicles passing a point and the time frame, selecting the time unit (hours, minutes, seconds).
- Enter the number of vehicles on a road segment and the segment length, selecting the length unit (km, miles, m, ft).
- Convert time to hours and segment length to kilometers if needed.
- Calculate the flow (\( q \)) in vehicles/hour.
- Calculate the density (\( k \)) in vehicles/km.
- Calculate the headway (\( h \)) in meters as the reciprocal of density.
- Calculate the average travel speed (\( s \)) using the fundamental equation.
- Convert the speed to the selected unit for display.
3. Importance of Traffic Density Calculation
Calculating traffic density and related metrics is crucial for:
- Traffic Management: Understanding congestion levels to optimize traffic flow.
- Road Safety: Estimating vehicle spacing to reduce collision risks.
- Planning: Designing road networks and traffic signals based on travel speeds and density.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1 (Based on Scenario): For \(\text{Vehicles Passing} = 20\), \(\text{Time} = 2 \, \text{minutes}\), \(\text{Vehicles on Segment} = 2\), \(\text{Segment Length} = 200 \, \text{m}\):
- Flow: \(\text{q} = \frac{20}{2/60} = 600 \, \text{veh/h}\)
- Density: \(\text{k} = \frac{2}{200/1000} = 10 \, \text{veh/km}\)
- Headway: \(\text{h} = \frac{1}{10} \times 1000 = 100 \, \text{m}\)
- Average Travel Speed: \(\text{s} = \frac{600}{10} = 60 \, \text{km/h}\)
- Example 2: For \(\text{Vehicles Passing} = 50\), \(\text{Time} = 5 \, \text{minutes}\), \(\text{Vehicles on Segment} = 3\), \(\text{Segment Length} = 1 \, \text{mile}\):
- Flow: \(\text{q} = \frac{50}{5/60} = 600 \, \text{veh/h}\)
- Convert: \(\text{Segment Length (km)} = 1 \times 1.60934 = 1.60934 \, \text{km}\)
- Density: \(\text{k} = \frac{3}{1.60934} = 1.86 \, \text{veh/km}\)
- Headway: \(\text{h} = \frac{1}{1.86} \times 1000 = 537.63 \, \text{m}\)
- Average Travel Speed: \(\text{s} = \frac{600}{1.86} = 322.58 \, \text{km/h}\)
- In mph: \(\text{s} = 322.58 \times 0.621371 = 200.49 \, \text{mph}\)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between flow and density?
A: Flow is the rate at which vehicles pass a point (vehicles/hour), while density is the number of vehicles per unit length of road (vehicles/km).
Q: Can density be zero?
A: Yes, if there are no vehicles on the segment, but this will result in an undefined speed (division by zero).
Q: How accurate is the speed calculation?
A: The calculation is accurate for the given inputs but assumes constant flow and density, which may vary in real-world conditions due to traffic patterns.
Traffic Density Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back