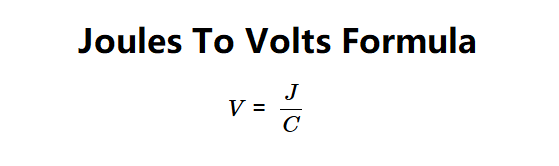1. What is Joules to Volts Converter?
Definition: This converter calculates the electric potential (voltage) in volts from energy in joules and charge in coulombs, using the relationship \( V = \frac{J}{C} \).
Purpose: It is used in electrical engineering and physics to determine the voltage across a charge given the energy transferred, supporting multiple units for energy, charge, and voltage.
2. How Does the Converter Work?
The converter uses the following formula:
Formula:
- Voltage: \[
V = \frac{J}{C}
\]
Where:
- \( V \): Voltage in volts (V)
- \( J \): Energy in joules (J)
- \( C \): Charge in coulombs (C)
Unit Conversions:
- Energy:
- 1 kJ = 1000 J
- 1 MJ = 1000000 J
- Charge:
- Voltage:
- 1 kV = 1000 V
- 1 mV = 0.001 V
Steps:
- Enter the energy and charge values, selecting their respective units (J/kJ/MJ for energy, C/mC for charge).
- Validate the inputs to ensure they are non-negative and charge is non-zero.
- Convert energy to joules and charge to coulombs.
- Calculate the voltage in volts using the formula.
- Convert the voltage to the selected output unit (V, kV, mV).
- Display the result, using scientific notation for values less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Joules to Volts Conversion
Converting joules to volts is crucial for:
- Electrical Engineering: Determines the voltage across a capacitor or other charge-storing device given the energy and charge.
- Physics Experiments: Calculates potential differences in electrostatics experiments.
- Energy Storage Systems: Helps in designing batteries and capacitors by relating energy to voltage.
4. Using the Converter
Example:
Convert 100 J of energy with a charge of 2 C to volts.
- Energy: 100 J, Charge: 2 C, Output unit: V.
- The converter calculates:
- Voltage: \( V = \frac{100}{2} = 50.0000 \, \text{V} \)
- The converter returns:
Another Example:
Convert 5 kJ of energy with a charge of 10 mC to millivolts.
- Energy: 5 kJ, Charge: 10 mC, Output unit: mV.
- The converter calculates:
- Convert energy to J: \( 5 \times 1000 = 5000 \, \text{J} \)
- Convert charge to C: \( 10 \times 0.001 = 0.01 \, \text{C} \)
- Voltage in V: \( V = \frac{5000}{0.01} = 500000.0000 \, \text{V} \)
- Voltage in mV: \( 500000 \times 1000 = 500000000.0000 \, \text{mV} \)
- The converter returns:
- Voltage: 500000000.0000 mV
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the Joules to Volts Converter?
A: The Joules to Volts Converter calculates the voltage from energy and charge using the formula \( V = \frac{J}{C} \), supporting multiple units for flexibility.
Q: Why is charge required for this conversion?
A: Voltage is defined as energy per unit charge, so the charge value is necessary to compute the potential difference.
Q: How is the Joules to Volts Converter used in real life?
A: It is used in electrical engineering to design circuits, in physics to analyze electrostatic systems, and in energy storage to calculate voltages in capacitors and batteries.
Joules to Volts Converter© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back