1. What is a Horsepower to Voltage Calculator?
Definition: This calculator determines the voltage (V) required for a motor or device given its horsepower (HP), current (in mA, A, or kA), efficiency, power factor, and current type.
Purpose: It is used in electrical engineering to design circuits, select power supplies, and ensure safe motor operation by calculating the necessary voltage.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator rearranges Ohm’s Law-based formulas to solve for voltage, adjusted for efficiency and power factor:
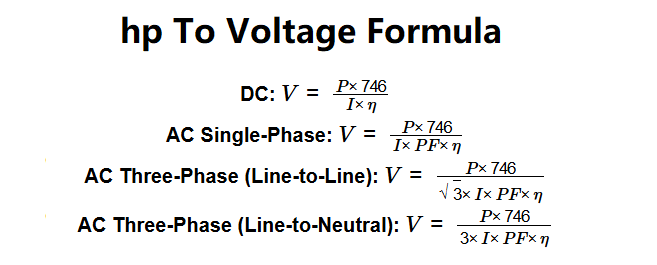
DC: \( V = \frac{P \times 746}{I \times \eta} \)
AC Single-Phase: \( V = \frac{P \times 746}{I \times PF \times \eta} \)
AC Three-Phase (Line-to-Line): \( V = \frac{P \times 746}{\sqrt{3} \times I \times PF \times \eta} \)
AC Three-Phase (Line-to-Neutral): \( V = \frac{P \times 746}{3 \times I \times PF \times \eta} \)
Where:
- \( V \) is the voltage (volts)
- \( P \) is the power (horsepower, converted to electrical hp)
- \( I \) is the current (amps, converted from mA, A, or kA)
- \( \eta \) is the efficiency (decimal, e.g., 0.9 for 90%)
- \( PF \) is the power factor (0 to 1)
- 746 converts electrical HP to watts
Steps:
- Enter the horsepower (\( P \)) and select a unit (hp(I), hp(M), hp(E), hp(S))
- Enter the current (\( I \)) and select a unit (mA, A, kA)
- Enter the efficiency (\( \eta \)) as a percentage
- Enter the power factor (\( PF \)) for AC systems
- Select the current type (DC, AC Single-Phase, AC Three-Phase)
- Select the desired voltage unit (mV, V, kV, MV)
- Convert horsepower to electrical horsepower and current to amps
- Calculate the voltage using the appropriate formula
- Convert the result to the selected voltage unit
Display format:
- If the voltage is > 10000 or < 0.0001 (and not zero), use scientific notation (e.g., \( 1.23456e-3 \))
- Otherwise, display with 5 decimal places
3. Importance of HP to Voltage Calculation
Details: Accurate voltage calculations are critical for selecting appropriate power supplies, ensuring motor compatibility, and preventing electrical issues like undervoltage or overvoltage in industrial and residential systems.
4. Using the Calculator
Tips: Input positive values for all fields. For DC, power factor is not used (assumed 1). Efficiency and power factor significantly affect AC results—use realistic values (e.g., 80-95% for efficiency, 0.8-0.9 for PF). Select the appropriate current unit (mA for small currents, kA for large systems).
Examples:
- DC Motor: \( P = 1 \, \text{hp(I)} \), \( I = 32711.06 \, \text{mA} \), \( \eta = 95\% \), Output in V:
- Convert: \( 1 \, \text{hp(I)} = 1 \times \frac{745.7}{746} = 0.99960 \, \text{hp(E)} \)
- Convert: \( 32711.06 \, \text{mA} \times 10^{-3} = 32.71106 \, \text{A} \)
- \( V = \frac{0.99960 \times 746}{32.71106 \times 0.95} = 24.00000 \, \text{V} \)
- AC Single-Phase: \( P = 2 \, \text{hp(M)} \), \( I = 8.36437 \, \text{A} \), \( \eta = 90\% \), \( PF = 0.85 \), Output in V:
- Convert: \( 2 \, \text{hp(M)} = 2 \times \frac{735.5}{746} = 1.97252 \, \text{hp(E)} \)
- \( V = \frac{1.97252 \times 746}{8.36437 \times 0.85 \times 0.9} = 230.00000 \, \text{V} \)
- AC Three-Phase (Line-to-Line): \( P = 10 \, \text{hp(S)} \), \( I = 0.16892 \, \text{kA} \), \( \eta = 93\% \), \( PF = 0.9 \), Output in kV:
- Convert: \( 10 \, \text{hp(S)} = 10 \times \frac{9812}{746} = 131.52815 \, \text{hp(E)} \)
- Convert: \( 0.16892 \, \text{kA} \times 1000 = 168.92 \, \text{A} \)
- \( V = \frac{131.52815 \times 746}{\sqrt{3} \times 168.92 \times 0.9 \times 0.93} = 400000.00000 \, \text{V} \)
- Convert: \( 400000 \, \text{V} \times 10^{-3} = 400.00000 \, \text{kV} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the different types of horsepower?
A: Mechanical (hp(I)), metric (hp(M)), electrical (hp(E)), and boiler (hp(S)) horsepower differ in their definitions and conversion factors to watts.
Q: Why include efficiency and power factor?
A: Efficiency accounts for energy losses in the motor, and power factor adjusts for AC power delivery efficiency, both critical for accurate voltage calculations.
Q: What’s the difference between line-to-line and line-to-neutral voltage?
A: Line-to-line is the voltage between two phases in a three-phase system; line-to-neutral is between one phase and neutral, affecting the voltage calculation.
Q: Why choose a current unit?
A: Current can vary widely (e.g., milliamps for small electronics, kiloamps for industrial systems), so the calculator allows flexible input units for convenience.
Horsepower to Voltage Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back