Roof Calculator - Calculate Roof Square Footage with Pitch
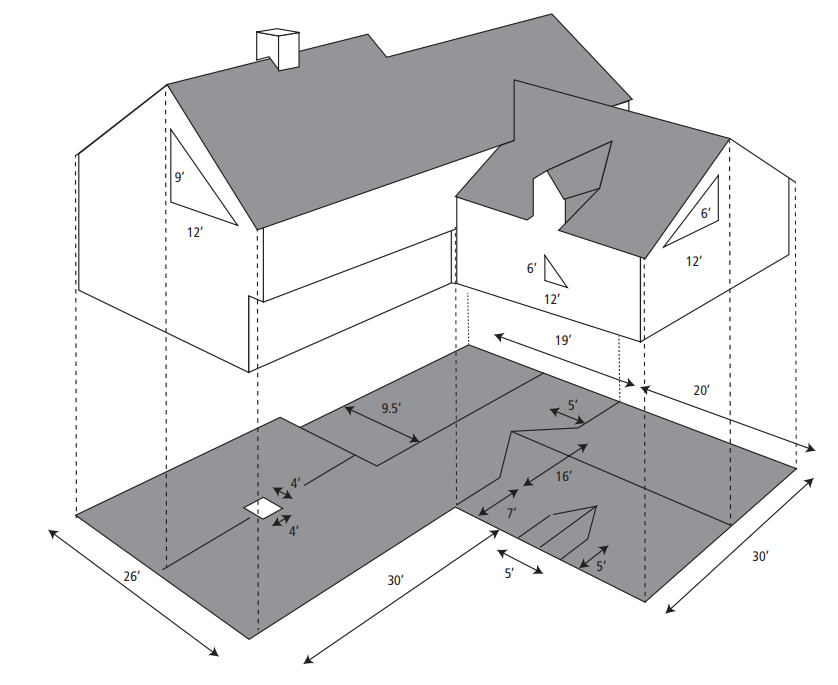
How to Calculate Roof Area
Step 1: Determine the dimensions (length and width) of each roof segment.
Step 2: Input these measurements into the calculator, choosing the correct units.
Step 3: Specify the roof pitch and select an appropriate waste percentage.
Step 4: Provide the cost per square (set to 0 by default).
Step 5: The tool will calculate the total area in square feet and the estimated cost.
Area calculation formula: $$\text{Total Area} = \sum (\text{Length} \times \text{Width} \times (1 + \text{Waste Percentage}) \times \text{Pitch Multiplier})$$
Cost calculation formula: $$\text{Total Cost} = \text{Total Area} \times \text{Cost per Square}$$
Guide to Roof Size Estimation
Before starting a roofing project, accurately assessing the roof's size is essential for determining material requirements.
In the U.S., roof measurements are typically in square feet, with contractors providing quotes based on this unit. For example, a 2,500-square-foot roof equates to 25 squares, where one square is 100 square feet.
The square footage of a house doesn’t directly correlate with its roof size. A 1,800-square-foot home might have a straightforward gable roof or a more intricate hip or mansard roof, each resulting in a different roof area.
Determining the Roof Base AreaTo estimate roof size, measure the base area of each section, factor in the pitch, compute the total square footage, and calculate the number of squares needed for materials.
Each roof section must be measured individually. A simple gable roof may have one section, while complex designs like cross-hip or gambrel roofs require measuring multiple segments.
Leveraging the Roofing Calculator
The calculator simplifies the process—just enter the length, width, and pitch to get the roof’s square footage.
Measuring Roof DimensionsFrom ground level, measure the roof’s length and width in feet, accounting for any overhangs beyond the house’s footprint.
Calculating Base AreaMultiply the length by the width (in feet) to find the base area of each section.
Adjusting for Roof PitchTo find the true roof area, adjust the base area using the roof pitch, which indicates the vertical rise per 12 inches of horizontal distance.
Typical pitches range from 4/12 to 8/12, though some sections may be steeper, like 18/12. Calculate each section separately if pitches vary.
For dual-pitch roofs, where each side has a different slope, compute each side’s area independently.
Applying Pitch MultipliersUse the pitch multiplier to adjust the base area. For instance, a 100-square-foot section with a 5/12 pitch:
100 × 1.083 = 108.3 square feet
Pitch Multipliers for Roof Area
These multipliers help convert base area to actual roof area based on pitch.
| Pitch (in/12) | Multiplier |
|---|---|
| 0/12 | 1.0000 |
| 1/12 | 1.0035 |
| 2/12 | 1.0138 |
| 3/12 | 1.0308 |
| 4/12 | 1.0541 |
| 5/12 | 1.0833 |
| 6/12 | 1.1180 |
| 7/12 | 1.1577 |
| 8/12 | 1.2019 |
| 9/12 | 1.2500 |
| 10/12 | 1.3017 |
| 11/12 | 1.3566 |
| 12/12 | 1.4142 |
| 13/12 | 1.4743 |
| 14/12 | 1.5366 |
| 15/12 | 1.6008 |
| 16/12 | 1.6667 |
| 17/12 | 1.7341 |
| 18/12 | 1.8028 |
| 19/12 | 1.8727 |
| 20/12 | 1.9437 |
| 21/12 | 2.0156 |
| 22/12 | 2.0883 |
| 23/12 | 2.1619 |
| 24/12 | 2.2361 |
Converting Area to Roofing Squares
Roofing projects are often quoted in squares, where one square equals 100 square feet. This unit helps estimate material needs accurately.
Divide the total roof area by 100 and round up to find the number of squares. For example, a 1,720-square-foot roof requires 18 squares.
 Home
Home Back
Back