1. What is the ACFM to SCFM Calculator?
Definition: This calculator converts the Actual Cubic Feet per Minute (ACFM) flow rate to the Standard Cubic Feet per Minute (SCFM) flow rate by adjusting for temperature and gauge pressure. SCFM standardizes the flow rate to a reference condition (typically 14.7 psia and 21°C or 294.15 K), making it useful for comparing gas flows under different conditions.
Purpose: It is used in engineering, particularly in HVAC, pneumatics, and industrial processes, to standardize gas flow rates for design, comparison, and performance evaluation of equipment like compressors and fans.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula:
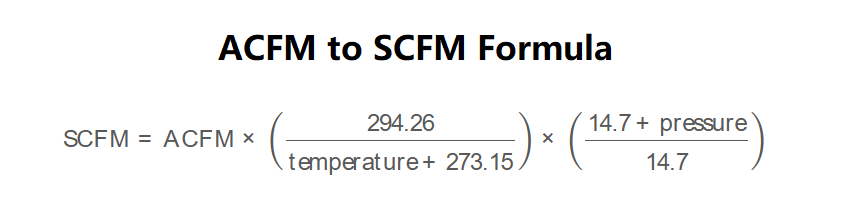
Formula:
\[
\text{SCFM} = \text{ACFM} \times \left( \frac{294.26}{\text{temperature} + 273.15} \right) \times \left( \frac{14.7 + \text{pressure}}{14.7} \right)
\]
where:
- \( \text{SCFM} \): Standard Cubic Feet per Minute (ft³/min, ft³/h, m³/s, L/min, m³/min)
- \( \text{ACFM} \): Actual Cubic Feet per Minute (ft³/min, ft³/h, m³/s, L/min, m³/min)
- \( \text{temperature} \): Temperature (°C, °F, K)
- \( \text{pressure} \): Gauge pressure (psig, barg, Pa, bar, psi, at, atm, Torr, hPa, kPa, lb/ft², mmHg, inHg)
Unit Conversions:
- Flow Rate (ACFM, SCFM):
- 1 ft³/min = 1 ft³/min
- 1 ft³/h = 1/60 ft³/min
- 1 m³/s = 2118.88 ft³/min
- 1 L/min = 0.0353147 ft³/min
- 1 m³/min = 35.3147 ft³/min
- Temperature:
- 1 °C = 1 °C
- 1 °F = (T - 32) × 5/9 °C
- 1 K = T - 273.15 °C
- Pressure (Gauge Pressure):
- 1 psig = 1 psig
- 1 barg = 14.5038 psig
- 1 Pa = 0.000145038 psig
- 1 bar = 14.5038 psig
- 1 psi = 1 psig
- 1 at = 14.2233 psig
- 1 atm = 14.6959 psig
- 1 Torr = 0.0193368 psig
- 1 hPa = 0.0145038 psig
- 1 kPa = 0.145038 psig
- 1 lb/ft² = 0.00694444 psig
- 1 mmHg = 0.0193368 psig
- 1 inHg = 0.491154 psig
Steps:
- Enter the actual flow rate (ACFM) in ft³/min, ft³/h, m³/s, L/min, or m³/min (default is 100 ft³/min, step size 0.00001).
- Enter the temperature in °C, °F, or K (default is 25°C, step size 0.00001).
- Enter the gauge pressure in psig, barg, Pa, bar, psi, at, atm, Torr, hPa, kPa, lb/ft², mmHg, or inHg (default is 0 psig, step size 0.00001).
- Convert the actual flow rate to ft³/min, temperature to Celsius (°C), and pressure to psig.
- Calculate the SCFM using the provided formula.
- Convert the SCFM to the selected unit and display the result, using scientific notation if the absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise rounded to 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of ACFM to SCFM Calculation
Converting ACFM to SCFM is crucial for:
- Industrial Applications: Standardizing gas flow rates ensures consistent performance evaluation of equipment like compressors, blowers, and fans, regardless of operating conditions.
- HVAC Systems: Designing ventilation systems requires standardized flow rates to ensure proper air delivery under varying temperatures and pressures.
- Engineering Design: SCFM provides a common reference for comparing gas flows, aiding in the selection and sizing of equipment in pneumatics and process engineering.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: Calculate the SCFM with an ACFM of 100 ft³/min, temperature of 25°C, and gauge pressure of 0 psig, in ft³/min:
- Enter ACFM = 100 ft³/min.
- Enter Temperature = 25 °C.
- Enter Gauge Pressure = 0 psig.
- Temperature factor: \( \frac{294.26}{25 + 273.15} = \frac{294.26}{298.15} = 0.9867 \).
- Pressure factor: \( \frac{14.7 + 0}{14.7} = 1 \).
- SCFM: \( 100 \times 0.9867 \times 1 = 98.6700 \, \text{ft}^3/\text{min} \).
- Result: \( \text{SCFM} = 98.6700 \, \text{ft}^3/\text{min} \).
- Example 2: Calculate the SCFM with an ACFM of 6000 ft³/h, temperature of 86°F, and gauge pressure of 1 barg, in ft³/h:
- Enter ACFM = 6000 ft³/h, convert to ft³/min: \( 6000 \div 60 = 100 \, \text{ft}^3/\text{min} \).
- Enter Temperature = 86 °F, convert to °C: \( (86 - 32) \times 5/9 = 30 \, \text{°C} \).
- Enter Gauge Pressure = 1 barg, convert to psig: \( 1 \times 14.5038 = 14.5038 \, \text{psig} \).
- Temperature factor: \( \frac{294.26}{30 + 273.15} = \frac{294.26}{303.15} = 0.9707 \).
- Pressure factor: \( \frac{14.7 + 14.5038}{14.7} = \frac{29.2038}{14.7} = 1.9866 \).
- SCFM: \( 100 \times 0.9707 \times 1.9866 = 192.8486 \, \text{ft}^3/\text{min} \).
- Convert to ft³/h: \( 192.8486 \times 60 = 11570.9160 \).
- Result: \( \text{SCFM} = 11570.9160 \, \text{ft}^3/\text{h} \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between ACFM and SCFM?
A: ACFM (Actual Cubic Feet per Minute) is the actual flow rate of a gas under specific temperature and pressure conditions. SCFM (Standard Cubic Feet per Minute) standardizes the flow rate to a reference condition (typically 14.7 psia and 21°C), allowing for consistent comparison across different operating conditions.
Q: Why adjust for temperature and pressure?
A: Gas volume changes with temperature and pressure. Higher temperatures expand the gas, increasing its volume, while higher pressures compress it, decreasing its volume. The SCFM formula adjusts the actual flow (ACFM) to standard conditions to provide a consistent measure of gas flow.
Q: What does gauge pressure mean in this context?
A: Gauge pressure is the pressure above atmospheric pressure, measured in psig (pounds per square inch gauge). In the formula, it is added to the standard atmospheric pressure (14.7 psia) to account for the total pressure affecting the gas flow.
ACFM to SCFM Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back