 Home
Home
 Back
Back
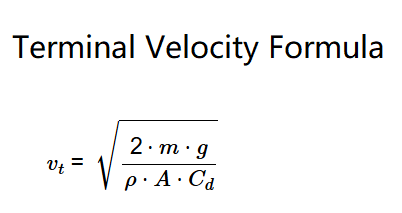
Definition: Terminal velocity is the constant maximum speed an object reaches when falling through a fluid, such as air or water, where the downward gravitational force is balanced by the upward drag force. At this point, the object no longer accelerates and moves at a steady speed.
Purpose: This concept is widely used to analyze the motion of falling objects, including skydivers, raindrops, or parachutes, in physics, engineering, and aerodynamics.
The calculator applies the terminal velocity formula:
Where:
Unit Conversions:
Explanation: Users input values in their chosen units, which are converted to SI units (kg, m/s², m², kg/m³). The calculator then computes terminal velocity and displays it in m/s, km/h, mph, and ft/s, ensuring accuracy and versatility.
Significance: Terminal velocity is critical for:
Guidelines: Input the object’s mass, gravitational acceleration (default 9.81 m/s²), cross-sectional area, fluid density (default 1.225 kg/m³ for air), and select a shape or custom drag coefficient. Ensure all values are positive. Results are displayed with 3 decimal places in m/s, km/h, mph, and ft/s.
Q: What happens if I enter negative values?
A: The calculator sets terminal velocity to 0 for invalid (negative or zero) inputs, as physical values must be positive.
Q: Why does terminal velocity vary for different shapes?
A: The drag coefficient (C_d) depends on shape, orientation, and surface texture, affecting how air resistance opposes gravity.
Q: Can this calculator be used for water instead of air?
A: Yes, adjust the fluid density (e.g., ~1000 kg/m³ for water) to calculate terminal velocity in different fluids.
Q: What is a typical terminal velocity for a skydiver?
A: A skydiver in a belly-to-earth position typically reaches ~55 m/s (about 200 km/h or 124 mph) in air.
Q: How accurate is the default fluid density?
A: The default 1.225 kg/m³ is for air at sea level (15°C, 1 atm), but it varies with altitude, temperature, and pressure—adjust as needed.