 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: This calculator computes the velocity of particles (e.g., electrons, protons) using kinetic energy, momentum, or mass and acceleration, applying classical or relativistic physics based on speed.
Purpose: It is used in particle physics, quantum mechanics, and high-energy physics to determine particle speeds in accelerators, cosmic rays, or material interactions.
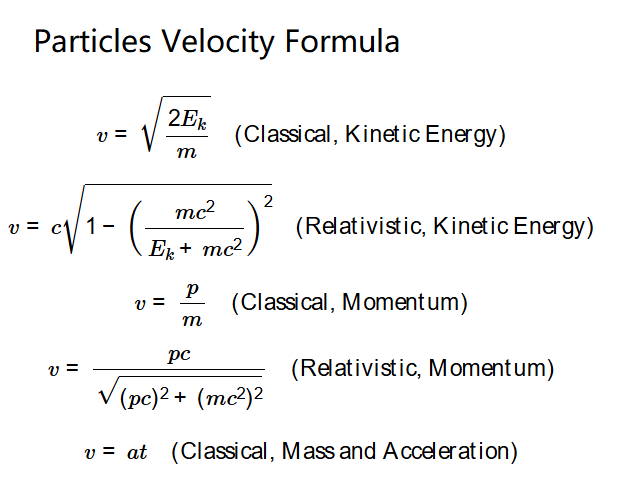
The calculator uses these formulas:
Explanation: Select a method, input values in your chosen units, and the calculator converts to base units (J, kg, kg·m/s, m/s², s), applies the appropriate formula, and outputs velocity in m/s, km/s, mph, % of \(c\), and Hz.
Unit Conversions:
Details: Particle velocity is crucial for understanding motion in physics. Examples include:
Applications: Essential for high-energy physics, radiation detection, and quantum mechanics.
Tips: Select a method, enter positive values with up to 4 decimal places, and choose units. Results are in m/s, km/s, mph, % of \(c\), and Hz. Values < 0.0001 use scientific notation. Avoid zero mass or invalid inputs. Relativistic formulas apply if speeds approach \(c\) (kinetic energy or momentum high relative to rest mass).
Example: For an electron with \(E_k = 1 \, \text{MeV}\), \(m = 0.511 \, \text{MeV}/c^2\):
Relativistic Energy: Total energy \(E = \gamma mc^2\), where \(\gamma = \frac{1}{\sqrt{1 - \frac{v^2}{c^2}}}\).
Relativistic Momentum: \(p = \gamma mv\), linked to velocity via mass and speed.
Particle Acceleration: \(a = \frac{F}{m}\), affecting velocity over time, used in the acceleration method.
Q: Why use relativistic formulas?
A: For speeds > 0.1% of \(c\), relativistic effects matter; the calculator switches automatically if kinetic energy or momentum indicates high speed.
Q: Can velocity exceed \(c\)?
A: No, relativistic formulas ensure \( v \leq c \).
Q: Why does the result show zero?
A: If mass is zero or inputs are invalid, results default to zero.
Q: Why are some results in scientific notation?
A: Values < 0.0001 are displayed as, e.g., \(1.23 \times 10^{-5}\), for clarity.
Q: What does Hz mean here?
A: Hz is included as \( v / 2\pi \), representing frequency (non-standard but per request), assuming a cyclical context.