 Home
Home
 Back
Back
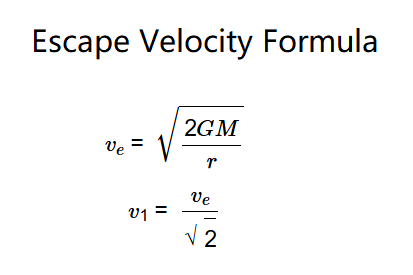
Definition: This calculator computes the escape velocity (\(v_e\)), the minimum speed needed to escape a celestial body’s gravity without further acceleration.
Purpose: It is used in astrophysics and space exploration to determine the speed required for spacecraft to leave planets, moons, or stars.
The calculator uses these formulas:
Explanation: Input mass and radius in your chosen units. The calculator converts to base units (kg, m) and outputs escape velocity and first cosmic velocity in m/s, km/s, mph, and Hz.
Unit Conversions:
Details: Escape velocity is critical for space travel and understanding gravitational fields. Examples include:
Applications: Essential for mission planning, satellite launches, and astrophysical modeling.
Tips: Enter positive values with up to 4 decimal places and select units. Results are in m/s, km/s, mph, and Hz (escape) plus m/s, km/s, mph (first cosmic). Values < 0.0001 use scientific notation. Avoid zero radius.
Example: For Earth (\(M = 1 \, \text{Earth} = 5.972 \times 10^{24} \, \text{kg}\), \(r = 1 \, \text{R⊕} = 6371 \, \text{km}\)):
First Cosmic Velocity: The speed for a circular orbit, \(v_1 = \frac{v_e}{\sqrt{2}}\), used by satellites.
Gravitational Potential: Energy per unit mass, \(U = -\frac{GM}{r}\), relates to escape energy.
Orbital Mechanics: Escape velocity exceeds orbital speeds, enabling interplanetary travel.
Q: What’s the difference between escape and first cosmic velocity?
A: Escape velocity (\(v_e\)) is for leaving gravity entirely; first cosmic velocity (\(v_1\)) is for orbiting.
Q: Can mass or radius be negative?
A: No, both must be positive for physical meaning.
Q: Why does the result show zero?
A: If radius is zero, division by zero occurs, so results default to zero.
Q: Why are some results in scientific notation?
A: Values < 0.0001 are displayed as, e.g., \(1.23 \times 10^{-5}\), for clarity.
Q: How do I use Earth or Sun units?
A: Enter the value (e.g., 1), select "Earths" or "Suns" for mass, or "R⊕" or "R☉" for radius, and it scales accordingly.