 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: The Weibull Distribution Calculator computes common measures (mean, median, mode, variance, skewness), probability density function, cumulative distribution function, or quantile function for a Weibull distribution, based on scale and shape parameters, and optional inputs.
Purpose: This tool helps analyze data with a Weibull distribution, common in reliability engineering, survival analysis, and wind speed modeling, where the distribution shape is flexible.
The calculator uses the following formulas:
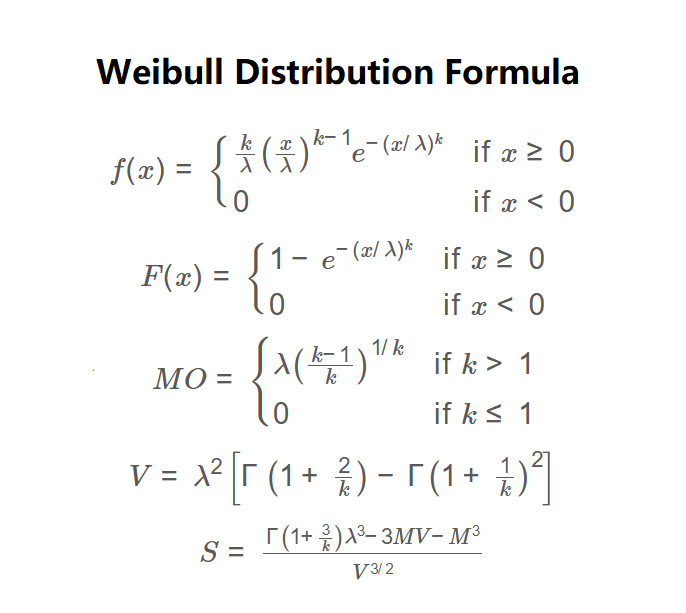
\( f(x) = \begin{cases} \frac{k}{\lambda} \left( \frac{x}{\lambda} \right)^{k-1} e^{-(x/\lambda)^k} & \text{if } x \geq 0 \\ 0 & \text{if } x < 0 \end{cases} \)
\( F(x) = \begin{cases} 1 - e^{-(x/\lambda)^k} & \text{if } x \geq 0 \\ 0 & \text{if } x < 0 \end{cases} \)
\( P(X \leq x) = F(x), \quad P(X < x) = F(x), \quad P(X > x) = 1 - F(x), \quad P(X \geq x) = 1 - F(x) \)
\( Q(p) = \lambda (-\ln(1-p))^{1/k} \)
\( M = \lambda \Gamma\left(1 + \frac{1}{k}\right) \)
\( MD = \lambda (\ln 2)^{1/k} \)
\( MO = \begin{cases} \lambda \left( \frac{k-1}{k} \right)^{1/k} & \text{if } k > 1 \\ 0 & \text{if } k \leq 1 \end{cases} \)
\( V = \lambda^2 \left[ \Gamma\left(1 + \frac{2}{k}\right) - \Gamma\left(1 + \frac{1}{k}\right)^2 \right] \)
\( S = \frac{\Gamma\left(1 + \frac{3}{k}\right) \lambda^3 - 3 M V - M^3}{V^{3/2}} \)
Where:
Steps:
Calculating Weibull distribution properties is essential for:
Example (Common Measures): Calculate measures with λ = 2, k = 2:
Example (Probability Density Function): Calculate PDF with λ = 2, k = 2, x = 1.5:
Example (Cumulative Distribution Function): Calculate CDF with λ = 2, k = 2, x = 1.5:
Example (Quantile Function): Calculate quantile with λ = 2, k = 2, p = 0.5:
Q: What is the Weibull distribution?
A: The Weibull distribution is a continuous probability distribution used to model time-to-failure, survival times, or wind speeds, with flexible shape due to its parameters.
Q: What do λ and k represent?
A: The scale parameter λ stretches the distribution, and the shape parameter k determines its shape (exponential, Rayleigh, etc.).
Q: When is the Weibull distribution used?
A: It’s used in reliability engineering for failure analysis, survival analysis for time-to-event data, and meteorology for wind speed modeling.