 Home
Home
 Back
Back
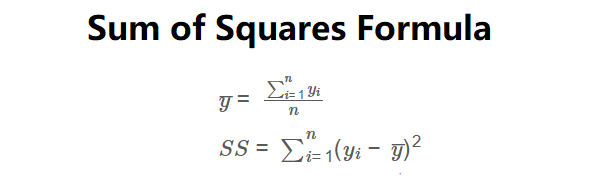
Definition: The Sum of Squares Calculator computes the sum of squared deviations (\( SS \)) from the sample mean, which measures the total variability in a dataset.
Purpose: This tool is used in statistics to quantify variability, serving as a building block for variance, standard deviation, and other analyses like ANOVA.
The calculator uses the following formulas for a dataset with \( n \) observations:
\( \bar{y} = \frac{\sum_{i=1}^n y_i}{n} \)
\( SS = \sum_{i=1}^n (y_i - \bar{y})^2 \)
Steps:
The sum of squares is critical for:
Example: Calculate the sum of squares for the dataset: [20, 22, 18].
Q: What does the sum of squares represent?
A: It measures the total squared deviation of data points from the mean, indicating dataset variability.
Q: Why is at least one data point required?
A: The sum of squares requires a mean to compute deviations, which can be defined with one data point (though variability is zero in such cases).
Q: How is the sum of squares used in statistics?
A: It’s a key component in calculating variance, standard deviation, and in analyses like regression and ANOVA to assess data spread.