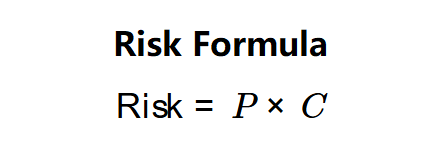1. What is a Risk Calculator?
Definition: This calculator estimates the risk associated with an event based on its probability of failure and the consequence of that failure.
Purpose: It assists in decision-making by quantifying potential risks in areas like finance, safety, or project management.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the formula:
\( \text{Risk} = P \times C \)
Where:
- \( P \): Probability of Failure (as a decimal, input as a percentage).
- \( C \): Consequence of Failure (e.g., monetary value or severity score).
- \( \text{Risk} \): The calculated risk value, reflecting the expected impact.
Steps:
- Input the probability of failure (as a percentage) and the consequence of failure.
- Validate: Probability between 0% and 100%, consequence non-negative.
- Calculate the risk as the product of probability and consequence.
- Round to 4 decimal places and display the result.
3. Importance of Risk Calculations
These calculations are key for:
- Financial Planning: Assessing investment risks.
- Safety Assessment: Evaluating potential hazards.
- Project Management: Identifying contingency needs.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Probability = 12%, Consequence = 2000 (e.g., investment loss):
- \( \text{Risk} = 0.12 \times 2000 = 240.0000 \).
- Result: 240.0000 (e.g., $240 expected loss).
- Probability = 7%, Consequence = 5000 (e.g., equipment failure cost):
- \( \text{Risk} = 0.07 \times 5000 = 350.0000 \).
- Result: 350.0000 (e.g., $350 expected cost).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What if the probability exceeds 100%?
A: The calculation is invalid, and an error is displayed.
Q: Can the consequence be zero?
A: Yes, it indicates no impact if the event occurs.
Q: What units should I use for consequence?
A: Any consistent unit (e.g., dollars, severity score) based on your context.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back