1. What is a Probability Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the probability of various scenarios involving two events A and B, assuming independence.
Purpose: It assists in understanding the likelihood of outcomes in games, experiments, or statistical analysis.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas (for independent events):
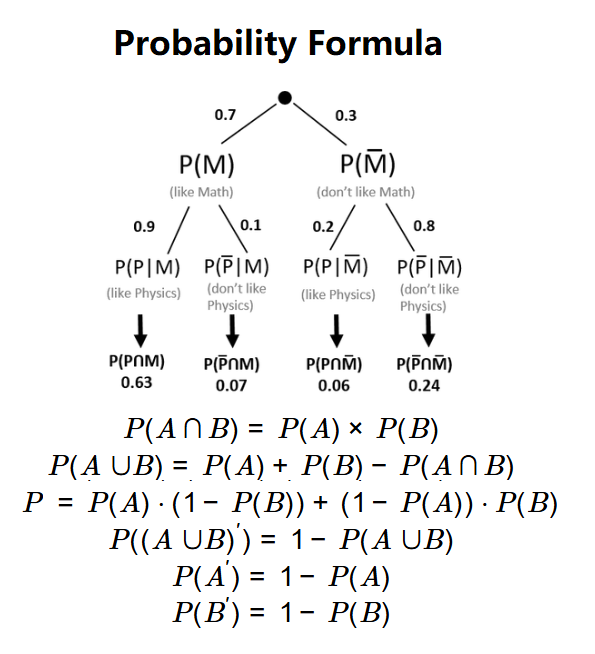
\( P(A \cap B) = P(A) \times P(B) \)
\( P(A \cup B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A \cap B) \)
\( P(\text{exactly one}) = P(A) \cdot (1 - P(B)) + (1 - P(A)) \cdot P(B) \)
\( P((A \cup B)') = 1 - P(A \cup B) \)
\( P(A') = 1 - P(A) \)
\( P(B') = 1 - P(B) \)
Steps:
- Input \( P(A) \) and \( P(B) \) as percentages.
- Select the desired probability scenario from the options.
- Validate: Probabilities must be between 0% and 100%.
- Calculate the selected probability using the appropriate formula.
- Convert to a percentage and round to 4 decimal places.
- Display the result or a table for all scenarios if "All" is selected.
3. Importance of Probability Calculations
These calculations are key for:
- Games and Gambling: Assessing combined event chances.
- Statistical Analysis: Predicting multiple event outcomes.
- Decision Making: Evaluating risks across scenarios.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples (P(A) = 50%, P(B) = 30%):
- A and B both occurring:
- \( P(A \cap B) = 0.5 \times 0.3 = 0.15 \).
- Result: 15.0000%.
- At least one of the events occurs:
- \( P(A \cup B) = 0.5 + 0.3 - 0.15 = 0.65 \).
- Result: 65.0000%.
- Exactly one of these events occurs:
- \( P(\text{exactly one}) = (0.5 \times 0.7) + (0.5 \times 0.3) = 0.35 + 0.15 = 0.5 \).
- Result: 50.0000%.
- Neither A nor B occurs:
- \( P((A \cup B)') = 1 - 0.65 = 0.35 \).
- Result: 35.0000%.
- A NOT occurring:
- \( P(A') = 1 - 0.5 = 0.5 \).
- Result: 50.0000%.
- B NOT occurring:
- \( P(B') = 1 - 0.3 = 0.7 \).
- Result: 70.0000%.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What if probabilities exceed 100%?
A: The calculation is invalid, and an error is displayed.
Q: Are A and B assumed independent?
A: Yes, the calculator assumes independence for all calculations.
Q: What does 'Neither' mean?
A: It’s the complement of at least one event occurring.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back