 Home
Home
 Back
Back
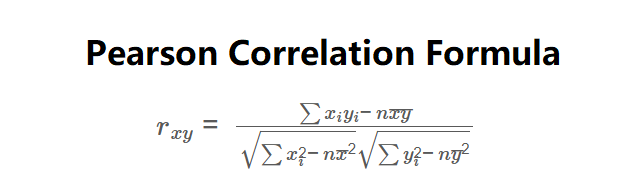
Definition: The Pearson Correlation Calculator computes the Pearson correlation coefficient (r), which measures the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two variables, X and Y.
Purpose: This tool is used in statistics to assess how well two datasets are linearly related, with values ranging from -1 (perfect negative correlation) to 1 (perfect positive correlation).
The calculator uses the following formula:
\( r_{xy} = \frac{\sum x_i y_i - n \bar{x} \bar{y}}{\sqrt{\sum x_i^2 - n \bar{x}^2} \sqrt{\sum y_i^2 - n \bar{y}^2}} \)
where \( x_i, y_i \) are the data points, \( \bar{x}, \bar{y} \) are the means, and \( n \) is the number of data points.
Steps:
The Pearson correlation coefficient is essential for:
Example: Calculate the Pearson correlation for X: [1, 3, 3, 5] and Y: [1, 2, 3, 4].
Q: What does the Pearson correlation coefficient indicate?
A: It measures the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two variables, with values from -1 (perfect negative) to 1 (perfect positive).
Q: Does a correlation of 0 mean no relationship?
A: No, it means no linear relationship. Non-linear relationships may exist. Independence implies \( r = 0 \), but the converse is only true for jointly normal variables.
Q: Why is at least 2 data points required?
A: Correlation measures relationships between pairs of points, so at least two points are needed to compute variance and covariance.