 Home
Home
 Back
Back
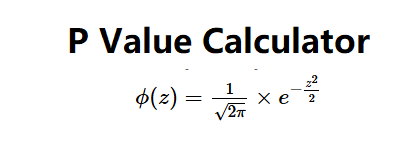
The p-value is the probability of observing a test statistic as extreme as the z-score under the null hypothesis. It is calculated by integrating the standard normal probability density function (PDF):
The cumulative distribution function (CDF), \( \Phi(z) \), is the integral of \( \phi(z) \) from \(-\infty\) to \( z \):
P-values are computed as:
This calculator uses numerical integration (trapezoidal rule) to approximate \( \Phi(z) \). P-values less than 0.00001 are displayed in scientific notation.
This calculator computes the p-value for a z-score using the integral of the standard normal distribution. It is ideal for statistical hypothesis testing in research, data analysis, or education.
Input the z-score and select the test type. The calculator numerically integrates the PDF to estimate the CDF and computes the p-value, which can be compared to a significance level (e.g., 0.05).
Example: Calculate the p-value for a z-score of 1.96 in a two-tailed test.
Use this tool for statistical analysis, A/B testing, or validating research hypotheses.
The following table provides approximate p-values for common z-scores in a two-tailed test:
| Z-Score | P-Value (Two-Tailed) |
|---|---|
| 1.00 | 0.3174 |
| 1.96 | 0.0500 |
| 2.58 | 0.0098 |
| 3.00 | 0.0027 |
Use this table for quick reference or to verify calculator results.
Below are frequently asked questions about P-Values: