 Home
Home
 Back
Back
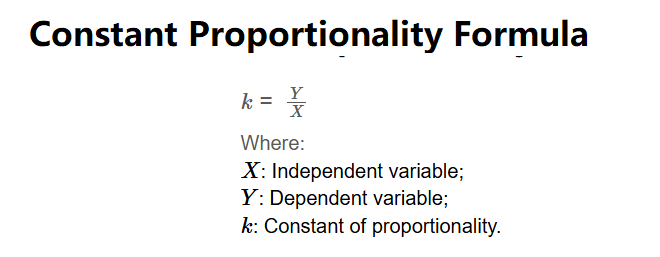
Definition: The Constant of Proportionality Calculator computes the constant of proportionality (\( k \)) for a linear relationship, defined as the ratio of the dependent variable (\( Y \)) to the independent variable (\( X \)).
Purpose: This tool is used to quantify the relationship between two variables in a direct proportion, commonly in mathematics, physics, and economics to model linear relationships like rates or scaling factors.
The calculator uses the following formula:
\( k = \frac{Y}{X} \)
Where:
Steps:
The constant of proportionality is essential for:
Example: Calculate the constant of proportionality for a linear relationship where \( X = 10 \) and \( Y = 20 \).
Q: What is the constant of proportionality?
A: It’s the ratio \( \frac{Y}{X} \) in a linear relationship where \( Y \) is directly proportional to \( X \).
Q: When is the constant of proportionality used?
A: It’s used to model direct proportions, such as in physics (e.g., speed), economics (e.g., unit pricing), or any linear relationship.
Q: Why can’t the independent variable be zero?
A: Division by zero is undefined, so \( X \neq 0 \) is required to compute \( k \).