1. What is a Bruce Protocol METs Calculator?
Definition: This calculator estimates the Heart Rate Maximum (HRmax), VO2 Max, and MET Max achieved during the Bruce Protocol treadmill test, based on sex, age, and the duration of the test.
Purpose: It helps athletes and medical professionals assess cardiovascular fitness and energy expenditure during the Bruce Protocol stress test.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
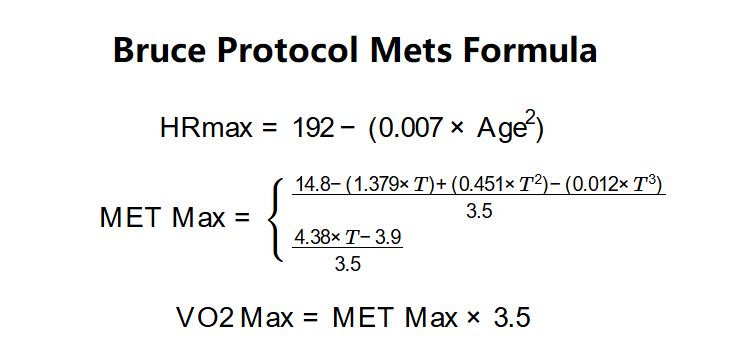
Heart Rate Maximum (HRmax):
\( \text{HRmax} = 192 - (0.007 \times \text{Age}^2) \)
This formula (Oakland Non-Linear) applies to both males and females.
MET Max:
\( \text{MET Max} =
\begin{cases}
\frac{14.8 - (1.379 \times T) + (0.451 \times T^2) - (0.012 \times T^3)}{3.5} & \text{(Male)} \\
\frac{4.38 \times T - 3.9}{3.5} & \text{(Female)}
\end{cases}
\)
Where \( T \) is the total time in minutes.
VO2 Max:
\( \text{VO2 Max} = \text{MET Max} \times 3.5 \)
VO2 Max is in mL/kg/min.
Steps:
- Select your Sex (Male or Female).
- Enter your Age in years.
- Enter the Time you completed the Bruce Protocol test in minutes.
- Validate inputs to ensure they are non-negative and logical (e.g., Age > 0).
- Compute HRmax based on age using the Oakland Non-Linear formula.
- Compute MET Max based on sex and time.
- Compute VO2 Max by multiplying MET Max by 3.5.
- Display HRmax, VO2 Max, and MET Max.
3. Importance of Bruce Protocol Calculations
These calculations are crucial for:
- Fitness Assessment: VO2 Max and MET Max measure cardiovascular fitness and endurance.
- Medical Evaluation: HRmax and VO2 Max are used in cardiac stress testing to assess heart function.
- Training Planning: Helps athletes tailor training intensity based on their maximum capacity.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1: A 30-year-old male completes the Bruce Protocol test for 10 minutes:
- Sex: Male
- Age: 30 years
- Time: 10 minutes
- HRmax: \( 192 - (0.007 \times 30^2) = 192 - (0.007 \times 900) = 192 - 6.3 = 185.7 \approx 186 \, \text{bpm} \)
- MET Max: \( \frac{14.8 - (1.379 \times 10) + (0.451 \times 10^2) - (0.012 \times 10^3)}{3.5} \)
- = \( \frac{14.8 - 13.79 + 45.1 - 12}{3.5} = \frac{34.11}{3.5} \approx 9.7 \, \text{METs} \)
- VO2 Max: \( 9.7 \times 3.5 = 33.95 \approx 34.0 \, \text{mL/kg/min} \)
- Result: HRmax = 186 bpm, VO2 Max = 34.0 mL/kg/min, MET Max = 9.7 METs
Example 2: A 25-year-old female completes the Bruce Protocol test for 8 minutes:
- Sex: Female
- Age: 25 years
- Time: 8 minutes
- HRmax: \( 192 - (0.007 \times 25^2) = 192 - (0.007 \times 625) = 192 - 4.375 = 187.625 \approx 188 \, \text{bpm} \)
- MET Max: \( \frac{4.38 \times 8 - 3.9}{3.5} = \frac{35.04 - 3.9}{3.5} = \frac{31.14}{3.5} \approx 8.9 \, \text{METs} \)
- VO2 Max: \( 8.9 \times 3.5 = 31.15 \approx 31.2 \, \text{mL/kg/min} \)
- Result: HRmax = 188 bpm, VO2 Max = 31.2 mL/kg/min, MET Max = 8.9 METs
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is VO2 Max?
A: VO2 Max is the maximum rate of oxygen consumption during intense exercise, measured in mL/kg/min, and indicates cardiovascular fitness.
Q: What is MET Max?
A: MET Max is the maximum Metabolic Equivalent of Task achieved, representing energy expenditure relative to resting metabolism (1 MET = 3.5 mL/kg/min).
Q: Why does MET Max differ between males and females?
A: Males and females have different physiological capacities for oxygen uptake, reflected by the different formulas used for MET Max calculation.
Bruce Protocol METs Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back