1. What is a Bike Cadence and Speed Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the speed of a bicycle based on the wheel size, tire size, gear ratio (chainring and cog sizes), and an assumed cadence (pedaling rate). It also displays the assumed cadence used in the calculation.
Purpose: It helps cyclists understand their speed for a given setup and cadence, aiding in training, gear selection, and performance optimization.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following steps:
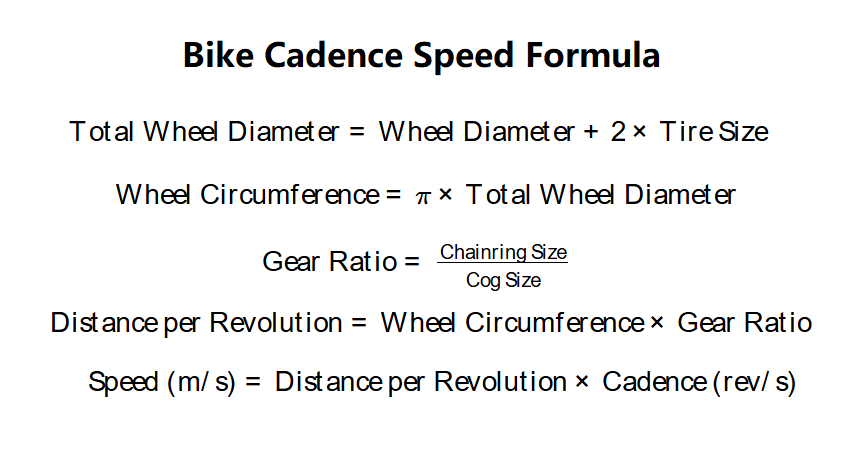
Step 1: Calculate Total Wheel Diameter:
\( \text{Total Wheel Diameter} = \text{Wheel Diameter} + 2 \times \text{Tire Size} \)
All measurements are converted to meters for consistency.
Step 2: Calculate Wheel Circumference:
\( \text{Wheel Circumference} = \pi \times \text{Total Wheel Diameter} \)
Step 3: Calculate Gear Ratio:
\( \text{Gear Ratio} = \frac{\text{Chainring Size}}{\text{Cog Size}} \)
Step 4: Calculate Distance per Pedal Revolution:
\( \text{Distance per Revolution} = \text{Wheel Circumference} \times \text{Gear Ratio} \)
Step 5: Calculate Speed:
\( \text{Speed (m/s)} = \text{Distance per Revolution} \times \text{Cadence (rev/s)} \)
Assumes a cadence of 90 RPM (1.5 rev/s). Speed is then converted to the selected unit (m/s, km/h, mph, ft/s), and cadence is displayed in the selected unit (RPM, rev/s).
Steps:
- Enter the Wheel Diameter, Tire Size, Chainring Size, and Cog Size with their respective units.
- Validate inputs to ensure they are non-negative and logical (e.g., Cog Size > 0).
- Compute the speed using an assumed cadence of 90 RPM.
- Display the cadence and speed, with dropdowns to change their units (RPM or rev/s for cadence; m/s, km/h, mph, ft/s for speed).
3. Importance of Cadence and Speed Calculation
Calculating cadence and speed is crucial for:
- Training Optimization: Helps cyclists determine their speed for a given cadence, aiding in setting training goals.
- Gear Selection: Allows cyclists to choose appropriate gears for desired speeds or terrains.
- Performance Monitoring: Enables tracking of speed improvements over time with consistent cadence.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1: A cyclist has a wheel diameter of 622 mm, tire size of 25 mm, chainring size of 50 teeth, cog size of 25 teeth, with cadence in RPM and speed in km/h:
- Wheel Diameter: 622 mm = 0.622 m
- Tire Size: 25 mm = 0.025 m
- Total Wheel Diameter: \( 0.622 + 2 \times 0.025 = 0.672 \, \text{m} \)
- Wheel Circumference: \( \pi \times 0.672 \approx 2.111 \, \text{m} \)
- Gear Ratio: \( \frac{50}{25} = 2 \)
- Distance per Revolution: \( 2.111 \times 2 = 4.222 \, \text{m} \)
- Speed (m/s): \( 4.222 \times 90 \times \frac{1}{60} = 6.333 \, \text{m/s} \)
- Speed (km/h): \( 6.333 \times 3.6 = 22.80 \, \text{km/h} \)
- Result: Cadence = 90.00 RPM, Speed = 22.80 km/h
Example 2: A cyclist has a wheel diameter of 26 in, tire size of 1 in, chainring size of 44 teeth, cog size of 16 teeth, with cadence in rev/s and speed in mph:
- Wheel Diameter: 26 in = \( 26 \times 0.0254 = 0.6604 \, \text{m} \)
- Tire Size: 1 in = \( 1 \times 0.0254 = 0.0254 \, \text{m} \)
- Total Wheel Diameter: \( 0.6604 + 2 \times 0.0254 = 0.7112 \, \text{m} \)
- Wheel Circumference: \( \pi \times 0.7112 \approx 2.234 \, \text{m} \)
- Gear Ratio: \( \frac{44}{16} = 2.75 \)
- Distance per Revolution: \( 2.234 \times 2.75 \approx 6.144 \, \text{m} \)
- Speed (m/s): \( 6.144 \times 90 \times \frac{1}{60} = 9.216 \, \text{m/s} \)
- Cadence (rev/s): \( 90 \times \frac{1}{60} = 1.50 \, \text{rev/s} \)
- Speed (mph): \( 9.216 \times 2.23694 \approx 20.62 \, \text{mph} \)
- Result: Cadence = 1.50 rev/s, Speed = 20.62 mph
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is cadence in cycling?
A: Cadence is the rate at which a cyclist pedals, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM) or revolutions per second (rev/s). A typical cadence for efficient cycling is around 80–100 RPM.
Q: Why is a default cadence used?
A: Since both cadence and speed are outputs, this calculator assumes a cadence of 90 RPM (a common value) to compute speed. You can adjust inputs to see how speed changes with different cadences.
Q: How does gear ratio affect speed?
A: A higher gear ratio (larger chainring or smaller cog) increases the distance per pedal revolution, resulting in higher speed for the same cadence, but requires more effort.
Bike Cadence and Speed Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back