 Home
Home
 Back
Back
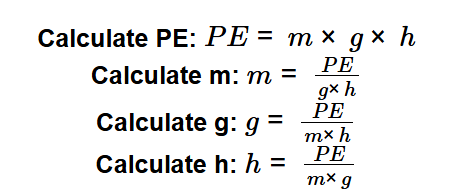
Definition: This calculator computes gravitational potential energy (PE) or related variables (mass, gravitational acceleration, or height) using the formula \( PE = m \times g \times h \). It allows users to calculate PE given mass (m), gravitational acceleration (g), and height (h), or solve for m, g, or h when the other variables are known.
Purpose: It is used in physics and engineering to analyze the energy stored in an object due to its position in a gravitational field, with applications in hydropower, roller coaster design, and space exploration, inspired by tools like CalculatorSoup’s Gravitational Potential Energy Calculator.
The calculator supports four calculation modes based on the formula:
Unit Conversions:
Details: Calculating gravitational potential energy is crucial for designing energy systems like hydropower plants, ensuring safety in amusement park rides, and understanding energy requirements in space missions.
Tips: Select the calculation mode, enter the required inputs with their units (e.g., mass in kg, height in m), ensuring mass, potential energy, and gravitational acceleration are positive, and height is non-negative for PE calculations (positive for m or g). Click “Calculate” to get the result in the selected unit. The result uses scientific notation for very small (< 0.0001) or large (> 100,000) values.
Given (Calculate PE, Large Values): Mass = 1000 kg, Gravitational Acceleration = 9.81 m/s², Height = 150 m.
Calculation: Convert units (all in SI): \( m = 1000 \, \text{kg} \), \( g = 9.81 \, \text{m/s}^2 \), \( h = 150 \, \text{m} \).
- \( PE = 1000 \times 9.81 \times 150 = 1471500 \, \text{J} \)
- In MJ: \( PE = 1471500 \times 0.000001 = 1.4715 \, \text{MJ} \)
- In kWh: \( PE = 1471500 \times (1/3600000) \approx 0.409 \, \text{kWh} \)
Result (> 100,000 for J): 1.471500e+06 J, 1.472 MJ, 0.409 kWh.