1. What is Voltage Regulation Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the voltage regulation (\( V_R \)) and percentage change (\( PC \)) of a voltage regulator, which can be either step-down (linear, buck) or step-up (boost, buck-boost).
Purpose: It is used in electrical engineering to evaluate the performance of voltage regulators by measuring how well they maintain a stable output voltage under varying load conditions.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas for voltage regulation:
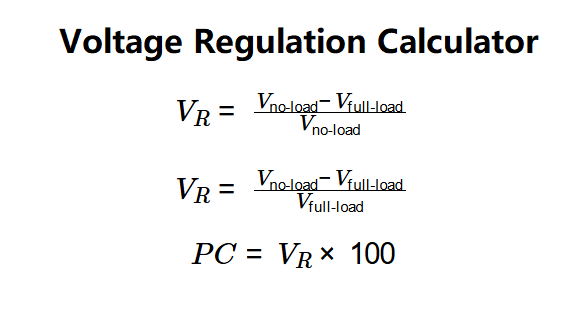
Step-Down Voltage Regulation (Linear, Buck):
- \( V_R = \frac{V_{\text{no-load}} - V_{\text{full-load}}}{V_{\text{no-load}}} \)
Step-Up Voltage Regulation (Boost, Buck-Boost):
- \( V_R = \frac{V_{\text{no-load}} - V_{\text{full-load}}}{V_{\text{full-load}}} \)
Percentage Change (Both Types):
- \( PC = V_R \times 100 \)
Where:
- \( V_R \): Voltage regulation (unitless);
- \( PC \): Percentage change (%);
- \( V_{\text{no-load}} \): No-load voltage (V);
- \( V_{\text{full-load}} \): Full-load voltage (V).
Steps:
- Select the regulator type (step-down or step-up).
- Enter the no-load voltage (\( V_{\text{no-load}} \)) and full-load voltage (\( V_{\text{full-load}} \)) with their units.
- Convert voltages to volts.
- Calculate the voltage regulation (\( V_R \)) using the appropriate formula based on the regulator type.
- Calculate the percentage change (\( PC \)) by multiplying \( V_R \) by 100.
- Display results in scientific notation if their absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Voltage Regulation Calculation
Calculating voltage regulation is crucial for:
- Power Supply Design: Ensuring that voltage regulators maintain a stable output voltage under varying load conditions, which is essential for reliable operation of electronic devices.
- Performance Evaluation: Assessing the efficiency and quality of voltage regulators in applications like power supplies, battery chargers, and DC-DC converters.
- System Optimization: Identifying the need for better regulation to minimize voltage fluctuations, improving the performance and longevity of electrical systems.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1 (Step-Down Regulation): Calculate the voltage regulation and percentage change for a step-down regulator with \( V_{\text{no-load}} = 12 \, \text{V} \) and \( V_{\text{full-load}} = 11.5 \, \text{V} \):
- Input Values:
- Regulator Type: Step-Down;
- \( V_{\text{no-load}} = 12 \, \text{V} \);
- \( V_{\text{full-load}} = 11.5 \, \text{V} \);
- Voltage Regulation: \( V_R = \frac{V_{\text{no-load}} - V_{\text{full-load}}}{V_{\text{no-load}}} = \frac{12 - 11.5}{12} \approx 0.0417 \);
- Percentage Change: \( PC = V_R \times 100 = 0.0417 \times 100 \approx 4.17\% \);
- Result: \( V_R = 4.1700e-2 \), \( PC = 4.1700\% \).
Example 2 (Step-Up Regulation): Calculate the voltage regulation and percentage change for a step-up regulator with \( V_{\text{no-load}} = 15 \, \text{V} \) and \( V_{\text{full-load}} = 14 \, \text{V} \):
- Input Values:
- Regulator Type: Step-Up;
- \( V_{\text{no-load}} = 15 \, \text{V} \);
- \( V_{\text{full-load}} = 14 \, \text{V} \);
- Voltage Regulation: \( V_R = \frac{V_{\text{no-load}} - V_{\text{full-load}}}{V_{\text{full-load}}} = \frac{15 - 14}{14} \approx 0.0714 \);
- Percentage Change: \( PC = V_R \times 100 = 0.0714 \times 100 \approx 7.14\% \);
- Result: \( V_R = 7.1400e-2 \), \( PC = 7.1400\% \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between step-down and step-up voltage regulation?
A: Step-down regulation (used in linear and buck regulators) measures the voltage drop from no-load to full-load relative to the no-load voltage, as the output voltage decreases with load. Step-up regulation (used in boost and buck-boost regulators) measures the voltage drop relative to the full-load voltage, as the output voltage is higher than the input.
Q: Why is voltage regulation important for power supplies?
A: Voltage regulation ensures that a power supply maintains a stable output voltage despite changes in load current, which is critical for the reliable operation of electronic devices and preventing damage due to voltage fluctuations.
Q: What does a high percentage change indicate?
A: A high percentage change (\( PC \)) indicates poor voltage regulation, meaning the regulator struggles to maintain a stable output voltage as the load changes. Ideally, \( PC \) should be low for good performance.
Voltage Regulation Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back