1. What is a Torsional Constant Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the torsional constant (\( K \)) for various cross-sectional shapes under torsion, using the shape's dimensions.
Purpose: It is used in engineering to analyze how a structural member resists twisting under torque, which is crucial for designing beams, shafts, and other components.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas for \( K \), depending on the shape:
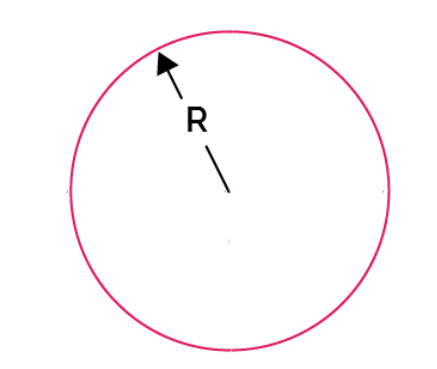
- Circle: \( K = \frac{\pi R^4}{2} \)
- Solid Ellipse: \( K = \frac{\pi a^3 b^3}{a^2 + b^2} \)
- Hollow Ellipse: \( K = \frac{\pi a^3 b^3 (1 - q^4)}{a^2 + b^2} \), where \( q = \frac{a_n}{a} = \frac{b_n}{b} \)
- Thin-Walled Ellipse: \( K = \frac{4 \pi^2 t (a - \frac{t}{2})^2 (b - \frac{t}{2})^2}{U} \), where \( U = \pi (a + b - t) t \left(1 + 0.258 \frac{(a - b)^2}{(a + b - t)^2}\right) \)
- Solid Square: \( K = \frac{9 a^4}{64} \)
- Solid Rectangle: \( K = \frac{a^3 b}{3} - 0.214 b^4 + 0.0175 \frac{b^8}{a^4} \)
- Thin-Walled Rectangle: \( K = \frac{2 t (a - t)^2 (b - t)^2}{a + b - t - t_1^2 - t^2} \)
- I-Section: \( K = 2 K_1 + K_2 + 2 \alpha D^4 \), where \( K_1 = \frac{a b^3}{3} - 0.21 b^4 + 0.0175 \frac{b^8}{a^4} \), \( K_2 = \frac{c d^3}{3} \), \( D = \frac{t_1}{b} (0.15 + 0.1 \frac{r}{b}) \), \( \alpha = \frac{t_1}{b} (0.15 + 0.1 \frac{r}{b}) \), and if \( b < d \), then \( \frac{t}{t_1} = \frac{b}{d} \), if \( d < b \), then \( \frac{t}{t_1} = \frac{d}{b} \)
Unit Conversions:
- Input Dimensions: m, cm (1 m = 100 cm), mm (1 m = 1000 mm)
- Torsional Constant (\( K \)): m⁴, cm⁴ (1 m⁴ = 10000 cm⁴), mm⁴ (1 m⁴ = 100000000 mm⁴)
Steps:
- Select a shape to display its formula and input the required dimensions with their units.
- Convert all dimensions to meters for calculation.
- Calculate \( K \) based on the shape's formula.
- Convert the result to the selected unit for display, using scientific notation for values less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Torsional Constant Calculation
Calculating the torsional constant is crucial for:
- Engineering Design: Ensuring structural members can resist twisting under applied torque.
- Material Selection: Choosing shapes with appropriate torsional properties.
- Safety: Preventing torsional failure in mechanical components like shafts and beams.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1 (Circle): For a circle with \( R = 10 \, \text{cm} \):
- Convert: \( R = 10 / 100 = 0.1 \, \text{m} \)
- Torsional Constant: \( K = \frac{\pi R^4}{2} = \frac{\pi \times 0.1^4}{2} = 0.0001571 \, \text{m}^4 \)
- Convert to cm⁴: \( K = 0.0001571 \times 10000 = 1.571 \, \text{cm}^4 \)
- Result: \( K = 1.571 \, \text{cm}^4 \)
- Example 2 (Thin-Walled Rectangle): For a thin-walled rectangle with \( a = 50 \, \text{mm} \), \( b = 30 \, \text{mm} \), \( t = 2 \, \text{mm} \), \( t_1 = 3 \, \text{mm} \):
- Convert: \( a = 50 / 1000 = 0.05 \, \text{m} \), \( b = 30 / 1000 = 0.03 \, \text{m} \), \( t = 2 / 1000 = 0.002 \, \text{m} \), \( t_1 = 3 / 1000 = 0.003 \, \text{m} \)
- Torsional Constant: \( K = \frac{2 \times 0.002 \times (0.05 - 0.002)^2 \times (0.03 - 0.002)^2}{0.05 + 0.03 - 0.002 - 0.003^2 - 0.002^2} = 6.024 \times 10^{-9} \, \text{m}^4 \)
- Convert to mm⁴: \( K = 6.024 \times 10^{-9} \times 100000000 = 0.6024 \, \text{mm}^4 \)
- Result: \( K = 0.6024 \, \text{mm}^4 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the torsional constant?
A: The torsional constant (\( K \)) is a geometric property of a cross-section that quantifies its resistance to torsion.
Q: Why is the torsional constant important?
A: It determines how much a member will twist under torque, which is critical for ensuring structural stability.
Torsional Constant Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back