1. What is Three-Phase Power Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the line current (\( I_{\text{line}} \)), line voltage (\( V_{\text{line}} \)), power factor (\( \text{PF} \)), apparent power (\( S \)), and reactive power (\( Q \)) in a three-phase electrical system, configured in either star (Y) or delta (D) connection.
Purpose: It is used in electrical engineering to analyze the electrical characteristics of three-phase systems, which are common in industrial and commercial power distribution for motors, transformers, and other heavy loads.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas for a three-phase system:
Relationships:
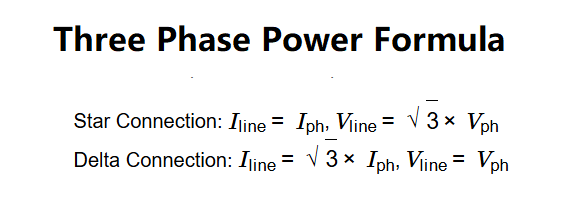
- Star Connection: \( I_{\text{line}} = I_{\text{ph}} \), \( V_{\text{line}} = \sqrt{3} \times V_{\text{ph}} \)
- Delta Connection: \( I_{\text{line}} = \sqrt{3} \times I_{\text{ph}} \), \( V_{\text{line}} = V_{\text{ph}} \)
- \( \text{PF} = \cos \varphi \)
- \( S = \sqrt{3} \times V_{\text{line}} \times I_{\text{line}} \)
- \( Q = \sqrt{3} \times V_{\text{line}} \times I_{\text{line}} \times \sin \varphi \)
Where:
- \( V_{\text{line}} \): Line voltage (V);
- \( I_{\text{line}} \): Line current (A);
- \( V_{\text{ph}} \): Phase voltage (V);
- \( I_{\text{ph}} \): Phase current (A);
- \( \text{PF} \): Power factor;
- \( \varphi \): Phase angle (degrees);
- \( S \): Apparent power (VA);
- \( Q \): Reactive power (VAR).
Steps:
- Select the connection type (Star/Y or Delta/D).
- Enter the phase voltage (\( V_{\text{ph}} \)), phase current (\( I_{\text{ph}} \)), and phase angle (\( \varphi \)) with their units.
- Convert phase voltage to volts and phase current to amperes.
- Convert phase values to line values based on the connection type.
- Calculate the power factor using \( \text{PF} = \cos \varphi \).
- Calculate the apparent power (\( S \)) and reactive power (\( Q \)) using the formulas above.
- Convert the line voltage, line current, and power values to the selected output units.
- Display results in scientific notation if their absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Three-Phase Power Calculation
Calculating electrical parameters in a three-phase system is crucial for:
- Power Distribution: Designing efficient power systems for industrial applications, where three-phase systems are standard due to their balanced load distribution.
- Equipment Sizing: Determining the voltage and current requirements for motors, transformers, and generators to ensure they operate within safe limits.
- Energy Management: Analyzing power factor and reactive power to optimize energy usage and improve efficiency in electrical grids.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1 (Star Connection): Calculate the parameters for a star-connected three-phase system with \( V_{\text{ph}} = 230 \, \text{V} \), \( I_{\text{ph}} = 10 \, \text{A} \), and \( \varphi = 30^\circ \):
- Input Values:
- Connection: Star;
- \( V_{\text{ph}} = 230 \, \text{V} \), so \( V_{\text{line}} = \sqrt{3} \times V_{\text{ph}} = \sqrt{3} \times 230 \approx 398.37 \, \text{V} \);
- \( I_{\text{ph}} = 10 \, \text{A} \), so \( I_{\text{line}} = I_{\text{ph}} = 10 \, \text{A} \);
- \( \varphi = 30^\circ \);
- Power Factor: \( \text{PF} = \cos \varphi = \cos 30^\circ \approx 0.866 \);
- Apparent Power: \( S = \sqrt{3} \times V_{\text{line}} \times I_{\text{line}} = \sqrt{3} \times 398.37 \times 10 \approx 6899.5 \, \text{VA} = 6.8995 \, \text{kVA} \);
- Reactive Power: \( \sin \varphi = \sin 30^\circ = 0.5 \), \( Q = \sqrt{3} \times V_{\text{line}} \times I_{\text{line}} \times \sin \varphi = 6899.5 \times 0.5 \approx 3449.75 \, \text{VAR} = 3.4498 \, \text{kVAR} \);
- Result: \( V_{\text{line}} = 398.3700 \, \text{V} \), \( I_{\text{line}} = 10.0000 \, \text{A} \), \( \text{PF} = 8.6600e-1 \), \( S = 6.8995 \, \text{kVA} \), \( Q = 3.4498 \, \text{kVAR} \).
Example 2 (Delta Connection): Calculate the parameters for a delta-connected three-phase system with \( V_{\text{ph}} = 230 \, \text{V} \), \( I_{\text{ph}} = 5 \, \text{A} \), and \( \varphi = 45^\circ \):
- Input Values:
- Connection: Delta;
- \( V_{\text{ph}} = 230 \, \text{V} \), so \( V_{\text{line}} = V_{\text{ph}} = 230 \, \text{V} \);
- \( I_{\text{ph}} = 5 \, \text{A} \), so \( I_{\text{line}} = \sqrt{3} \times I_{\text{ph}} = \sqrt{3} \times 5 \approx 8.66 \, \text{A} \);
- \( \varphi = 45^\circ \);
- Power Factor: \( \text{PF} = \cos \varphi = \cos 45^\circ \approx 0.707 \);
- Apparent Power: \( S = \sqrt{3} \times V_{\text{line}} \times I_{\text{line}} = \sqrt{3} \times 230 \times 8.66 \approx 3447.3 \, \text{VA} = 3.4473 \, \text{kVA} \);
- Reactive Power: \( \sin \varphi = \sin 45^\circ \approx 0.707 \), \( Q = \sqrt{3} \times V_{\text{line}} \times I_{\text{line}} \times \sin \varphi = 3447.3 \times 0.707 \approx 2437.24 \, \text{VAR} = 2.4372 \, \text{kVAR} \);
- Result: \( V_{\text{line}} = 230.0000 \, \text{V} \), \( I_{\text{line}} = 8.6600 \, \text{A} \), \( \text{PF} = 7.0700e-1 \), \( S = 3.4473 \, \text{kVA} \), \( Q = 2.4372 \, \text{kVAR} \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between star and delta connections in a three-phase system?
A: In a star (Y) connection, the line current equals the phase current, but the line voltage is \( \sqrt{3} \) times the phase voltage. In a delta (D) connection, the line voltage equals the phase voltage, but the line current is \( \sqrt{3} \) times the phase current. This affects how power is calculated.
Q: How does the phase angle affect the power factor and reactive power?
A: The phase angle (\( \varphi \)) determines the power factor (\( \text{PF} = \cos \varphi \)) and the reactive power component (\( \sin \varphi \)). A larger phase angle reduces the power factor and increases the reactive power, indicating a less efficient power transfer.
Q: Can this calculator be used for unbalanced three-phase systems?
A: No, this calculator assumes a balanced three-phase system where all phases have equal voltage and current. For unbalanced systems, individual phase calculations are required.
Three-Phase Power Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back