Thermal Stress and Force Calculator
Unit Converter ▲
Unit Converter ▼
1. What is the Thermal Stress and Force Calculator?
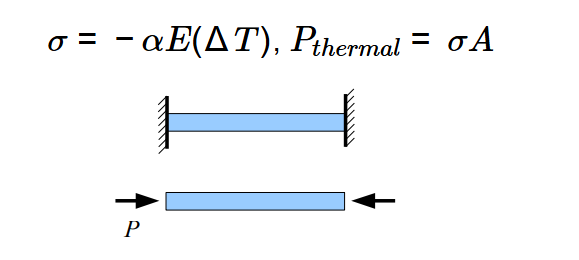
Definition: This calculator determines the thermal stress and force in a steel bar connecting two immovable concrete blocks due to a temperature change, using the formulas \(\sigma = -\alpha E (\Delta T)\) and \(P_{thermal} = \sigma A\).
Purpose: Helps assess stress and force in materials under thermal expansion or contraction.
Reference:Applied Strength of Materials for Engineering Technology
http://www.etcs.pfw.edu/~dupenb/ET_200/Applied%20Str%20of%20Mat%20for%20ET%20v14%20July%202018.pdf
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
Formulas:
\(\sigma = -\alpha E (\Delta T)\), \(P_{thermal} = \sigma A\)
Where:
- \(\sigma\): Thermal stress
- \(\alpha\): Coefficient of thermal expansion
- \(E\): Young's modulus
- \(\Delta T\): Temperature change (\(T_{final} - T_{initial}\))
- \(A\): Cross-sectional area
- \(P_{thermal}\): Thermal force
Steps:
- Step 1: Input Initial Temperature. Enter the starting temperature (e.g., 72°F).
- Step 2: Input Final Temperature. Enter the final temperature (e.g., 102°F).
- Step 3: Input Coefficient of Thermal Expansion. Enter \(\alpha\) (e.g., 0.0000065/°F).
- Step 4: Input Young's Modulus. Enter \(E\) (e.g., 30000000 psi).
- Step 5: Input Cross-Sectional Area. Enter \(A\) (e.g., 4 in²).
- Step 6: Calculate. The calculator computes the thermal stress and force.
3. Importance of Thermal Stress and Force Calculation
Calculating thermal stress and force is crucial for:
- Structural Integrity: Prevents failure due to thermal-induced stress.
- Material Design: Ensures compatibility with temperature changes.
- Unit Consistency: Supports conversions across units (e.g., °F to °C, psi to Pa, in² to cm²).
4. Using the Calculator
Example:
\( T_{initial} = 72°F \), \( T_{final} = 102°F \), \(\alpha = 0.0000065 \, /°F \), \( E = 30000000 \, psi \), \( A = 4 \, in^2 \):
- Step 1: \(\Delta T = 102 - 72 = 30 \, °F\).
- Step 2: \(\sigma = -0.0000065 \cdot 30000000 \cdot 30 \approx -5850 \, psi\).
- Step 3: \( P_{thermal} = -5850 \cdot 4 \approx -23400 \, lb \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why is the stress negative?
A: A negative value indicates compressive stress due to the bar being prevented from expanding.
Q: Can I use Celsius?
A: Yes, the calculator converts °C to °F internally to match the default \(\alpha\) unit.
Q: Is this accurate for all bar sizes?
A: Yes, if the cross-sectional area and material properties are correctly input.
Thermal Stress and Force Calculator© - All Rights Reserved
 Home
Home
 Back
Back