1. What is a Thermal Stress Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the thermal stress (\( \sigma_t \)) and change in temperature (\( \Delta T \)) in a material due to temperature changes, using the material's thermal expansion coefficient and Young's modulus.
Purpose: It is used in engineering to analyze how temperature changes induce stress in materials, which is crucial for designing structures that can withstand thermal expansion or contraction.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
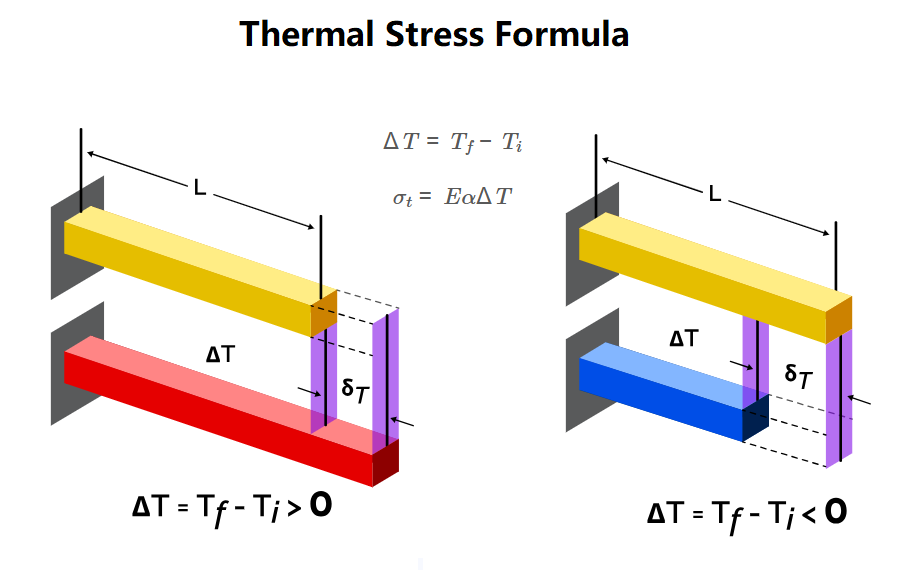
Change in Temperature:
\[
\Delta T = T_f - T_i
\]
Thermal Stress:
\[
\sigma_t = E \alpha \Delta T
\]
Where:
- \( \sigma_t \): Thermal stress (Pa, kPa, MPa, GPa, psi)
- \( \alpha \): Thermal expansion coefficient (/K)
- \( E \): Young's modulus (Pa, kPa, MPa, GPa, psi)
- \( \Delta T \): Change in temperature (°C, °F, K)
- \( T_i \): Initial temperature (°C, °F, K)
- \( T_f \): Final temperature (°C, °F, K)
Unit Conversions:
- Temperature (\( T_i, T_f, \Delta T \)): °C (K = °C + 273.15), °F (K = (°F - 32) × 5/9 + 273.15), K
- Young's Modulus (\( E \)): Pa, kPa (1 kPa = 1000 Pa), MPa (1 MPa = 1000000 Pa), GPa (1 GPa = 1000000000 Pa), psi (1 Pa = 0.000145038 psi, 1 psi = 6894.76 Pa)
- Thermal Stress (\( \sigma_t \)): Pa, kPa (1 kPa = 1000 Pa), MPa (1 MPa = 1000000 Pa), GPa (1 GPa = 1000000000 Pa), psi (1 Pa = 0.000145038 psi, 1 psi = 6894.76 Pa)
Steps:
- Select a material or choose "Custom" to input your own thermal expansion coefficient and Young's modulus.
- Enter the initial and final temperatures, and select their units.
- Convert all temperatures to Kelvin for calculation.
- Calculate \( \Delta T = T_f - T_i \).
- Calculate \( \sigma_t = E \alpha \Delta T \).
- Convert the results to the selected units for display, using scientific notation for values less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Thermal Stress Calculation
Calculating thermal stress is crucial for:
- Engineering Design: Ensuring materials can withstand stresses due to temperature changes.
- Material Selection: Choosing materials with appropriate thermal properties for specific applications.
- Safety: Preventing structural failures in buildings, bridges, and machinery due to thermal expansion or contraction.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1 (Concrete): For Concrete (\( \alpha = 0.00001 \, \text{/K} \), \( E = 27 \, \text{GPa} \)), \( T_i = 25 \, \text{°C} \), \( T_f = 120 \, \text{°C} \), stress in MPa:
- Convert: \( T_i = 25 + 273.15 = 298.15 \, \text{K} \), \( T_f = 120 + 273.15 = 393.15 \, \text{K} \), \( E = 27 \times 1000000000 = 27000000000 \, \text{Pa} \)
- Change in Temperature: \( \Delta T = 393.15 - 298.15 = 95.0000 \, \text{K} \)
- Thermal Stress: \( \sigma_t = 27000000000 \times 0.00001 \times 95 = 25650000 \, \text{Pa} \)
- Convert to MPa: \( \sigma_t = 25650000 \div 1000000 = 25.6500 \, \text{MPa} \)
- Result: \( \Delta T = 95.0000 \, \text{°C} \), \( \sigma_t = 25.6500 \, \text{MPa} \)
- Example 2 (Aluminum, Custom Units): For Aluminum (\( \alpha = 0.0000231 \, \text{/K} \), \( E = 68 \, \text{GPa} \)), \( T_i = 77 \, \text{°F} \), \( T_f = 248 \, \text{°F} \), stress in psi:
- Convert: \( T_i = (77 - 32) \times 5/9 + 273.15 = 298.15 \, \text{K} \), \( T_f = (248 - 32) \times 5/9 + 273.15 = 393.15 \, \text{K} \), \( E = 68 \times 1000000000 = 68000000000 \, \text{Pa} \)
- Change in Temperature: \( \Delta T = 393.15 - 298.15 = 95.0000 \, \text{K} \)
- Thermal Stress: \( \sigma_t = 68000000000 \times 0.0000231 \times 95 = 149226000 \, \text{Pa} \)
- Convert to psi: \( \sigma_t = 149226000 \div 6894.76 = 21637.5000 \, \text{psi} \)
- Convert \( \Delta T \) to °F: \( \Delta T = 95 \times 9/5 = 171.0000 \, \text{°F} \)
- Result: \( \Delta T = 171.0000 \, \text{°F} \), \( \sigma_t = 21637.5000 \, \text{psi} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is thermal stress?
A: Thermal stress is the stress induced in a material due to a change in temperature, caused by the material's tendency to expand or contract.
Q: What is the thermal expansion coefficient?
A: It is a material property that quantifies how much a material expands per unit temperature increase, measured in /K.
Q: Why does thermal stress occur?
A: Thermal stress occurs when a material is constrained and cannot freely expand or contract with temperature changes, leading to internal stresses.
Thermal Stress Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back