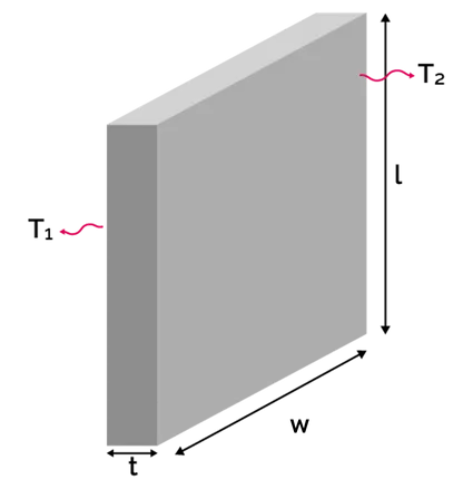
1. What is the Thermal Resistance Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the thermal resistance (\( R \)) for different geometries (Plate, Hollow Cylinder, Hollow Sphere) based on material properties and dimensions. Thermal resistance measures how much a material resists the flow of heat, given in units like K/W.
Purpose: It is used in thermal engineering to analyze heat transfer in systems like walls, pipes, and spherical containers, helping in the design of insulation, heat exchangers, and other thermal management systems.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following thermal resistance formulas:
Formulas:
- Plate: \[
R_{\text{plate}} = \frac{t}{k A}
\]
- Hollow Cylinder: \[
R_{\text{cylinder}} = \frac{\ln(r_2 / r_1)}{2 \pi k L}
\]
- Hollow Sphere: \[
R_{\text{sphere}} = \frac{r_2 - r_1}{4 \pi r_1 r_2 k}
\]
where:
- \( R_{\text{plate}}, R_{\text{cylinder}}, R_{\text{sphere}} \): Thermal resistance in K/W, °C/W, or °F·hr/Btu
- \( k \): Thermal conductivity in W/(m·K), W/(m·°C), or Btu/(hr·ft·°F)
- \( t \): Thickness of the plate in mm, cm, m, in, ft
- \( A \): Cross-sectional area in mm², cm², m², in², ft²
- \( r_1, r_2 \): Inner and outer radii in mm, cm, m, in, ft
- \( L \): Length of the cylinder in mm, cm, m, in, ft
Unit Conversions:
- Length (\( t, L, r_1, r_2 \)):
- 1 mm = 0.001 m
- 1 cm = 0.01 m
- 1 m = 1 m
- 1 in = 0.0254 m
- 1 ft = 0.3048 m
- Area (\( A \)):
- 1 mm² = \( 1 \times 10^{-6} \, \text{m}^2 \)
- 1 cm² = \( 1 \times 10^{-4} \, \text{m}^2 \)
- 1 m² = 1 m²
- 1 in² = 0.00064516 m²
- 1 ft² = 0.092903 m²
- Thermal Conductivity (\( k \)):
- W/(m·K): No conversion needed
- W/(m·°C): Same as W/(m·K) for ΔT
- Btu/(hr·ft·°F) to W/(m·K): Multiply by 1.730735
- Thermal Resistance (\( R \)):
- K/W: No conversion needed
- °C/W: Same as K/W for ΔT
- °F·hr/Btu: Multiply K/W by 0.176110
Steps:
- Select the geometry (Plate, Hollow Cylinder, or Hollow Sphere).
- Choose a material from the dropdown or select "Custom" to enter a custom thermal conductivity (\( k \)) in W/(m·K), W/(m·°C), or Btu/(hr·ft·°F).
- For Plate: Enter the thickness (\( t \)) and cross-sectional area (\( A \)).
- For Hollow Cylinder: Enter the inner radius (\( r_1 \)), outer radius (\( r_2 \)), and length (\( L \)).
- For Hollow Sphere: Enter the inner radius (\( r_1 \)) and outer radius (\$ r_2 \)).
- Convert all inputs to SI units (meters for lengths, m² for area, W/(m·K) for \( k \)).
- Calculate the thermal resistance using the appropriate formula.
- Convert the result to the selected unit (K/W, °C/W, or °F·hr/Btu) and display it, using scientific notation if the absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise rounded to 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Thermal Resistance Calculation
Calculating thermal resistance is crucial for:
- Thermal Design: It helps in designing efficient insulation for buildings, pipes, and equipment by understanding how materials resist heat flow.
- Heat Transfer Analysis: Used in heat exchanger design to optimize heat transfer rates.
- Material Selection: Allows engineers to select materials with appropriate thermal properties for specific applications, such as high-conductivity materials for heat sinks or low-conductivity materials for insulation.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1 (Plate): Calculate the thermal resistance of a glass window with a thickness of 5 mm and an area of 1 m²:
- Select Geometry: Plate.
- Select Material: Glass (\( k = 0.78 \, \text{W/(m·K)} \)).
- Enter Thickness = 5 mm, convert to m: \( 5 \times 0.001 = 0.005 \, \text{m} \).
- Enter Area = 1 m².
- Thermal Resistance: \( R = \frac{t}{k A} = \frac{0.005}{0.78 \times 1} = 0.0064103 \, \text{K/W} \).
- Result: \( R = 0.0064 \, \text{K/W} \).
- Example 2 (Hollow Cylinder): Calculate the thermal resistance of a copper pipe with an inner radius of 1 cm, outer radius of 1.2 cm, and length of 1 m:
- Select Geometry: Hollow Cylinder.
- Select Material: Copper (\( k = 401 \, \text{W/(m·K)} \)).
- Enter Inner Radius = 1 cm, convert to m: \( 1 \times 0.01 = 0.01 \, \text{m} \).
- Enter Outer Radius = 1.2 cm, convert to m: \( 1.2 \times 0.01 = 0.012 \, \text{m} \).
- Enter Length = 1 m.
- Thermal Resistance: \( R = \frac{\ln(r_2 / r_1)}{2 \pi k L} = \frac{\ln(0.012 / 0.01)}{2 \pi \times 401 \times 1} = 7.249 \times 10^{-5} \, \text{K/W} \).
- Result: \( R = 7.249 \times 10^{-5} \, \text{K/W} \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is thermal resistance?
A: Thermal resistance (\( R \)) quantifies how much a material or structure resists the flow of heat, defined as the temperature difference per unit of heat flow rate, typically in K/W.
Q: Why is thermal conductivity important?
A: Thermal conductivity (\( k \)) determines how well a material conducts heat. High \( k \) materials (e.g., copper) are used for heat transfer, while low \( k \) materials (e.g., glass fibre) are used for insulation.
Q: What are some real-world applications of thermal resistance?
A: Thermal resistance is critical in designing building insulation (e.g., walls, windows), heat exchangers (e.g., pipes), and thermal management systems in electronics (e.g., heat sinks).
Thermal Resistance Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back