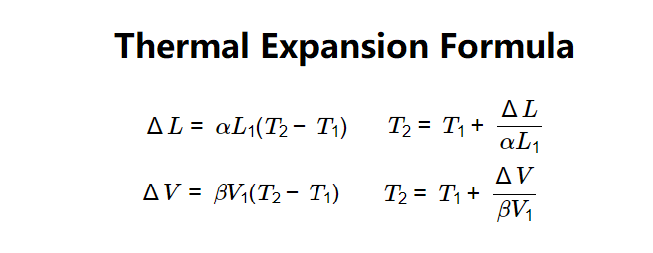Thermal Expansion Calculator - Calculate the Change in Temperature
Unit Converter ▲
Unit Converter ▼
1. What is the Thermal Expansion Calculator?
Definition: The Thermal Expansion Calculator determines the change in temperature (ΔT) causing a given deflection (δ) using the formula \( \delta = \alpha \cdot L \cdot \Delta T \), based on deflection (δ), length (L), and thermal expansion coefficient (α).
Purpose: Assists engineers and scientists in calculating temperature changes that lead to material expansion or contraction, aiding in structural design and safety assessments.
Reference:Applied Strength of Materials for Engineering Technology
http://www.etcs.pfw.edu/~dupenb/ET_200/Applied%20Str%20of%20Mat%20for%20ET%20v14%20July%202018.pdf
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
Formula:
\( \Delta T = \frac{\delta}{\alpha \cdot L} \)
Where:
- \( \Delta T \): Change in temperature (°F or °C)
- \( \delta \): Deflection (in or cm)
- \( \alpha \): Thermal expansion coefficient (/in/°F or /m/°C)
- \( L \): Length (ft or m)
Steps:
- Step 1: Input Deflection. Enter the deflection value (e.g., 0.06 in or cm).
- Step 2: Input Length. Enter the length of the material (e.g., 8 ft or m).
- Step 3: Input Thermal Expansion Coefficient. Enter the coefficient (e.g., 5×10⁻⁶ /in/°F).
- Step 4: Calculate. The calculator computes the temperature change.
3. Importance of Thermal Expansion Calculation
Calculating thermal expansion is crucial for:
- Structural Integrity: Prevents damage due to expansion or contraction.
- Design Safety: Ensures materials withstand temperature changes.
- Unit Consistency: Supports both metric (cm, m, °C) and imperial (in, ft, °F) units.
4. Using the Calculator
Example:
Deflection = 0.06 in, Length = 8 ft, α = 5×10⁻⁶ /in/°F:
- Step 1: \( \delta = 0.06 \) in.
- Step 2: \( L = 8 \) ft = 96 in.
- Step 3: \( \alpha = 5 \times 10^{-6} \) /in/°F.
- Step 4: \( \Delta T = \frac{0.06}{5 \times 10^{-6} \cdot 96} \approx 125 \) °F.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is thermal expansion?
A: Thermal expansion is the increase in size of a material due to a rise in temperature.
Q: Why use different units?
A: The calculator supports metric (cm, m, °C) and imperial (in, ft, °F) units for versatility.
Q: Is this calculator accurate for all materials?
A: Accuracy depends on the correct thermal expansion coefficient; consult material data sheets.
Thermal Expansion Calculator© - All Rights Reserved
 Home
Home
 Back
Back