1. What is Thermal Energy Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the average kinetic energy (\( KE \)) of gas molecules, their average speed (\( v \)), and the total thermal energy (\( U \)) of the gas, based on its molar mass, temperature, and number of moles.
Purpose: It is used in physics and thermodynamics to analyze the thermal properties of an ideal gas, aiding in the study of gas behavior, heat transfer, and energy distribution in systems like engines or atmospheric models.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
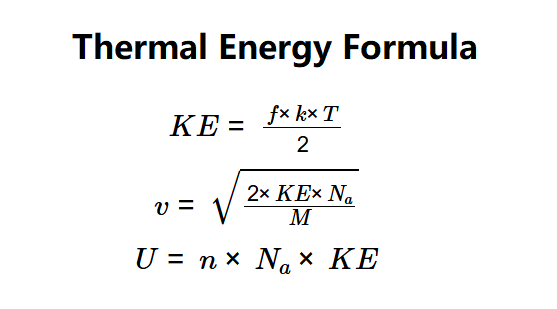
- \( KE = \frac{f \times k \times T}{2} \)
- \( v = \sqrt{\frac{2 \times KE \times N_a}{M}} \)
- \( U = n \times N_a \times KE \)
Where:
- \( KE \): Average kinetic energy (J);
- \( v \): Average speed (m/s);
- \( U \): Total thermal energy (J);
- \( f \): Degrees of freedom (set to 3 for a monatomic gas);
- \( k \): Boltzmann constant (\( 1.38064852 \times 10^{-23} \, \text{J/K} \));
- \( T \): Temperature (K);
- \( N_a \): Avogadro constant (\( 6.022140857 \times 10^{23} \, \text{1/mol} \));
- \( M \): Molar mass (kg/mol);
- \( n \): Number of moles (mol).
Steps:
- Enter the molar mass (\( M \)), temperature (\( T \)), and moles of gas (\( n \)) with their respective units.
- Convert inputs to base units (kg/mol for molar mass, K for temperature).
- Calculate \( KE \), \( v \), and \( U \) using the formulas.
- Convert the results to the selected units for each output.
- Display the results with unit selectors, formatted in scientific notation if the absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Thermal Energy Calculation
Calculating thermal energy and related properties is crucial for:
- Gas Behavior Analysis: Understanding the motion and energy of gas molecules, which is essential for studying thermodynamic processes.
- Heat Transfer: Analyzing how thermal energy is distributed in gases, aiding in the design of heat exchangers and engines.
- Physics Education: Demonstrating the kinetic theory of gases and the relationship between temperature, energy, and molecular motion.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1 (Air at 300 K): Calculate the thermal properties of air:
- Molar Mass: \( M = 28.96 \, \text{g/mol} \);
- Temperature: \( T = 300 \, \text{K} \);
- Moles of Gas: \( n = 1 \, \text{mol} \);
- Convert molar mass: \( M = 28.96 / 1000 = 0.02896 \, \text{kg/mol} \);
- Average Kinetic Energy: \( KE = \frac{3 \times 1.38064852 \times 10^{-23} \times 300}{2} \approx 6.21291834 \times 10^{-21} \, \text{J} \);
- Average Speed: \( v = \sqrt{\frac{2 \times 6.21291834 \times 10^{-21} \times 6.022140857 \times 10^{23}}{0.02896}} \approx 717.1236 \, \text{m/s} \);
- Total Thermal Energy: \( U = 1 \times 6.022140857 \times 10^{23} \times 6.21291834 \times 10^{-21} \approx 3741.48 \, \text{J} \);
- Convert results:
- \( KE \) in meV: \( 6.21291834 \times 10^{-21} / 1.60218 \times 10^{-22} \approx 38.769 \, \text{meV} \);
- \( v \) in ft/s: \( 717.1236 \times 3.28084 \approx 2352.6482 \, \text{ft/s} \);
- \( U \) in J: \( 3741.48 \, \text{J} \).
- Result: \( KE = 3.8769 \times 10^{1} \, \text{meV} \), \( v = 2352.6482 \, \text{ft/s} \), \( U = 3741.4800 \, \text{J} \).
Example 2 (Oxygen at 25°C): Calculate with different units:
- Molar Mass: \( M = 0.032 \, \text{kg/mol} \) (Oxygen);
- Temperature: \( T = 25 \, \text{°C} \);
- Moles of Gas: \( n = 2 \, \text{mol} \);
- Convert temperature: \( T = 25 + 273.15 = 298.15 \, \text{K} \);
- Average Kinetic Energy: \( KE = \frac{3 \times 1.38064852 \times 10^{-23} \times 298.15}{2} \approx 6.175813 \times 10^{-21} \, \text{J} \);
- Average Speed: \( v = \sqrt{\frac{2 \times 6.175813 \times 10^{-21} \times 6.022140857 \times 10^{23}}{0.032}} \approx 681.9754 \, \text{m/s} \);
- Total Thermal Energy: \( U = 2 \times 6.022140857 \times 10^{23} \times 6.175813 \times 10^{-21} \approx 7437.86 \, \text{J} \);
- Convert results:
- \( KE \) in meV: \( 6.175813 \times 10^{-21} / 1.60218 \times 10^{-22} \approx 38.535 \, \text{meV} \);
- \( v \) in ft/s: \( 681.9754 \times 3.28084 \approx 2237.4339 \, \text{ft/s} \);
- \( U \) in J: \( 7437.86 \, \text{J} \).
- Result: \( KE = 3.8535 \times 10^{1} \, \text{meV} \), \( v = 2237.4339 \, \text{ft/s} \), \( U = 7437.8600 \, \text{J} \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is thermal energy in a gas?
A: Thermal energy (\( U \)) in a gas is the total internal energy due to the random motion of its molecules, primarily kinetic energy in an ideal gas, calculated as \( U = n \times N_a \times KE \).
Q: Why is the number of degrees of freedom set to 3?
A: The calculator assumes a monatomic ideal gas, which has 3 translational degrees of freedom (\( f = 3 \)). For diatomic or polyatomic gases, \( f \) would be higher, but this requires additional input not specified here.
Q: What units can I use for the outputs?
A: Average kinetic energy can be in meV, J, kJ, cal, kcal, or eV. Average speed can be in ft/s, m/s, km/h, or mph. Total thermal energy can be in J, kJ, MJ, Wh, kWh, MWh, cal, kcal, BTU, MMBTU, or thm.
Thermal Energy Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back