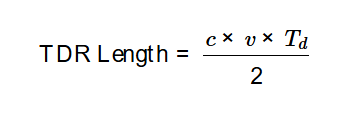1. What is TDR Length?
Definition: Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) length is the distance a signal travels along a cable or medium before reflecting back, calculated based on the time delay of the reflection and the signal's propagation speed.
Purpose: This calculator determines the length of a cable or medium using TDR, which is critical for diagnosing faults, measuring cable lengths, and analyzing transmission lines in RF and telecommunications systems.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula for TDR length:
TDR Length:
\[
\text{TDR Length} = \frac{c \times v \times T_d}{2}
\]
Where:
- TDR Length: Length of the cable or medium (converted to m, cm, or mm)
- \( c \): Speed of light (\( 3 \times 10^8 \, \text{m/s} \))
- \( v \): Velocity factor (unitless, typically between 0 and 1)
- \( T_d \): Time delay (converted to seconds from s, ms, µs, or ns)
Steps:
- Enter the velocity factor \( v \), typically provided by the cable manufacturer.
- Enter the time delay \( T_d \) and select its unit (s, ms, µs, ns).
- Click "Calculate" to compute the TDR length.
- Select the output unit for TDR length (m, cm, mm) in the result section.
- The result is displayed with 4 decimal places, or in scientific notation if less than 0.001.
3. Importance of TDR Length Calculations
TDR length calculations are essential for:
- Cable Fault Diagnosis: Identifies the location of faults, such as breaks or shorts, in cables.
- Transmission Line Analysis: Measures the length of cables or PCB traces in RF systems.
- Network Installation: Verifies cable lengths during installation and maintenance of communication networks.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: Coaxial Cable with 100 ns Delay
- \( v = 0.66 \), \( T_d = 100 \, \text{ns} = 100 \times 10^{-9} \, \text{s} \)
- TDR Length: \( \frac{3 \times 10^8 \times 0.66 \times 100 \times 10^{-9}}{2} = 9.9000 \, \text{m} \)
- Example 2: PCB Trace with 500 ps Delay (Length in mm)
- \( v = 0.5 \), \( T_d = 500 \, \text{ps} = 500 \times 10^{-12} \, \text{s} \)
- TDR Length: \( \frac{3 \times 10^8 \times 0.5 \times 500 \times 10^{-12}}{2} = 0.0375 \, \text{m} \)
- In mm: \( 0.0375 \times 1000 = 37.5000 \)
- Example 3: Fiber Optic Cable with 1 µs Delay (Length in cm)
- \( v = 0.68 \), \( T_d = 1 \, \text{µs} = 1 \times 10^{-6} \, \text{s} \)
- TDR Length: \( \frac{3 \times 10^8 \times 0.68 \times 1 \times 10^{-6}}{2} = 102.0000 \, \text{m} \)
- In cm: \( 102 \times 100 = 10200.0000 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR)?
A: TDR is a measurement technique that uses reflections of a signal to determine the characteristics of a transmission line, such as its length or the location of faults.
Q: What is the velocity factor?
A: The velocity factor (\( v \)) is the ratio of the speed of a signal in a medium to the speed of light in a vacuum, typically between 0 and 1, depending on the material properties.
Q: Why is the time delay divided by 2 in the formula?
A: The time delay \( T_d \) represents the round-trip time (to the reflection point and back). Dividing by 2 gives the one-way distance to the reflection point.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back