 Home
Home
 Back
Back
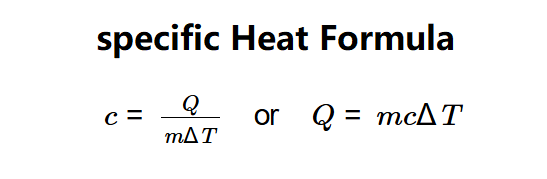
Definition: This calculator can compute either the specific heat capacity (\( c \)) of a material or the heat (\( Q \)) required to change its temperature, based on the formula \( c = \frac{Q}{m \Delta T} \) or \( Q = m c \Delta T \).
Purpose: It is used in physics, engineering, and thermodynamics to analyze the thermal properties of materials or the heat energy involved in heating/cooling processes, aiding in the design of thermal systems and material testing.
The calculator uses the specific heat formula:
Where:
Steps:
Calculating specific heat or heat energy is crucial for:
Example 1 (Calculating Heat for Argon): Calculate the heat required to change the temperature of Argon:
Example 2 (Calculating Specific Heat): Calculate the specific heat capacity of a material:
Q: What is specific heat capacity?
A: Specific heat capacity (\( c \)) is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a material by 1 Kelvin (or 1°C), reflecting the material's ability to store thermal energy.
Q: What does the temperature difference represent?
A: The temperature difference (\( \Delta T \)) is the change in temperature (\( T_f - T_i \)), which determines the amount of heat absorbed or released by the material.
Q: Why can I calculate either \( c \) or \( Q \)?
A: The formula \( Q = m c \Delta T \) can be rearranged to solve for either \( c \) or \( Q \), depending on which variable you need to find, making the calculator versatile for different applications.