1. What is Space Dynamics Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the specific angular momentum (\( h \)) of an elliptical orbit around Earth or the specific impulse (\( I_{sp} \)) of a rocket engine.
Purpose: It is used in aerospace engineering to analyze orbital mechanics (specific angular momentum) and rocket performance (specific impulse), aiding in the design of orbits and propulsion systems.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator supports two modes:
Formulas:
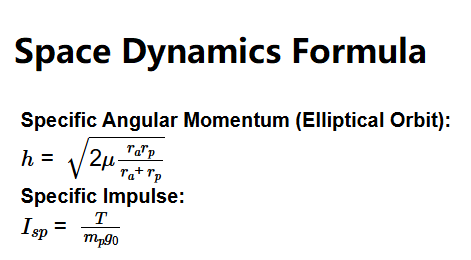
- Specific Angular Momentum (Elliptical Orbit):
- \( h = \sqrt{2 \mu \frac{r_a r_p}{r_a + r_p}} \)
- Specific Impulse:
- \( I_{sp} = \frac{T}{\dot{m}_p g_0} \)
Where:
- \( h \): Specific angular momentum (km²/s)
- \( \mu \): Gravitational parameter (\( \mu = G M \), for Earth \( \mu = 398600.418 \, \text{km}^3/\text{s}^2 \))
- \( r_a \): Apogee radius (km)
- \( r_p \): Perigee radius (km)
- \( I_{sp} \): Specific impulse (s)
- \( T \): Thrust (N)
- \( \dot{m}_p \): Propellant consumption rate (kg/s)
- \( g_0 \): Standard gravity (\( g_0 = 9.80665 \, \text{m/s}^2 \))
Unit Conversions:
- Apogee/Perigee Radius (\( r_a \), \( r_p \)):
- 1 km = 1 km
- 1 m = 0.001 km
- 1 mi = 1.60934 km
- Specific Angular Momentum (\( h \)):
- 1 km²/s = 1 km²/s
- 1 m²/s = 10⁶ km²/s
- 1 mi²/s = (0.621371)² km²/s
- Thrust (\( T \)):
- 1 N = 1 N
- 1 kN = 1000 N
- 1 lbf = 4.44822 N
- Propellant Consumption Rate (\( \dot{m}_p \)):
- 1 kg/s = 1 kg/s
- 1 g/s = 0.001 kg/s
- 1 lb/s = 0.453592 kg/s
Steps:
- Select the calculation mode (Specific Angular Momentum or Specific Impulse).
- Enter the required parameters with their respective units.
- Convert all inputs to base units (km for radii, N for thrust, kg/s for consumption rate).
- Calculate the result using the appropriate formula.
- Convert the result to the selected unit for display (for specific angular momentum).
- Display the result with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of These Calculations
These calculations are crucial for:
- Orbital Mechanics: Specific angular momentum (\( h \)) helps determine the shape and energy of an orbit, essential for mission planning.
- Rocket Performance: Specific impulse (\( I_{sp} \)) measures the efficiency of a rocket engine, aiding in engine selection and design.
- Space Missions: Accurate orbital parameters and engine performance metrics ensure successful satellite deployment and spacecraft maneuvers.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1 (Specific Angular Momentum):
Calculate the specific angular momentum for an elliptical orbit around Earth with an apogee radius of \( r_a = 10000 \, \text{km} \) and a perigee radius of \( r_p = 7000 \, \text{km} \).
- Select the mode as "Specific Angular Momentum".
- Enter \( r_a = 10000 \, \text{km} \), \( r_p = 7000 \, \text{km} \).
- The calculator computes:
- \( h = \sqrt{2 \cdot 398600.418 \cdot \frac{10000 \cdot 7000}{10000 + 7000}} \approx \sqrt{2 \cdot 398600.418 \cdot \frac{70000000}{17000}} \approx 57249.8226 \, \text{km}^2/\text{s} \).
Example 2 (Specific Impulse):
Calculate the specific impulse for a rocket engine producing a thrust of \( T = 50000 \, \text{N} \) with a propellant consumption rate of \( \dot{m}_p = 20 \, \text{kg/s} \).
- Select the mode as "Specific Impulse".
- Enter \( T = 50000 \, \text{N} \), \( \dot{m}_p = 20 \, \text{kg/s} \).
- The calculator computes:
- \( I_{sp} = \frac{50000}{20 \cdot 9.80665} \approx 255.1020 \, \text{s} \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is specific angular momentum?
A: Specific angular momentum (\( h \)) is the angular momentum per unit mass of an orbiting object, given by \( h = \sqrt{2 \mu \frac{r_a r_p}{r_a + r_p}} \) for an elliptical orbit.
Q: What is specific impulse?
A: Specific impulse (\( I_{sp} \)) measures the efficiency of a rocket engine, defined as the thrust per unit rate of propellant consumption, given by \( I_{sp} = \frac{T}{\dot{m}_p g_0} \).
Q: How does the calculator handle different units?
A: The calculator allows users to input radii in km, m, or mi; thrust in N, kN, or lbf; and consumption rate in kg/s, g/s, or lb/s. It converts all inputs to base units for calculation and displays specific angular momentum in user-selected units (km²/s, m²/s, mi²/s). Specific impulse is always in seconds.
Space Dynamics Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back